Industrial Lenses for Machine Vision Systems in 2026

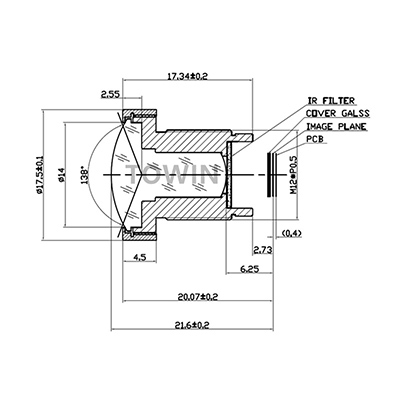
12mm 1/3″ CCTV M12 Pinhole lens
01/08/2026
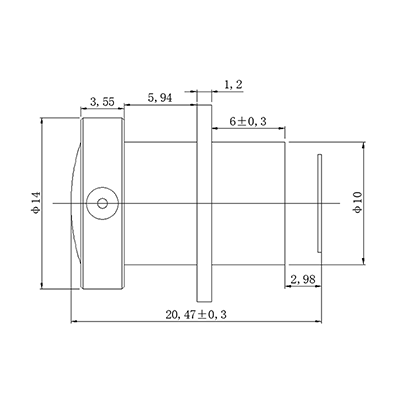
2.8mm M12 wide angle lens for IMX290 5MP
01/09/2026Table of Contents
Introduction
The deepening implementation of Industry 4.0 drives the upgrading of intelligent manufacturing, where machine vision systems have become the core of inspection and quality control. As a critical optical component, industrial lenses directly determine imaging quality and inspection accuracy. In 2026, high pixelation, intelligence, and customization will be the main industry trends, leading to a surge in demand for high-resolution lenses. The popularization of liquid lenses and telecentric lenses expands application boundaries, while high-end industries continue to raise requirements for lens precision and environmental adaptability.
With a wide variety of industrial lenses available, enterprises commonly face pain points such as low selection efficiency and parameter mismatch. Combining 2026 technical trends and mainstream scenarios, this guide sorts out core selection parameters, processes, industry-specific solutions, and TOWIN product analyses to provide a scientific selection framework, helping enterprises accurately match requirements and balance performance with cost.
Key Core Parameters to Evaluate First
1. Sensor Size and Image Circle Compatibility
| Parameter | Critical Considerations | 2026 Best Practices |
| Sensor Size | Must match lens specifications (1/2.3″, 1/1.8″, 2/3″, 1″, 4/3″, APS-C, Full Frame) | Always verify lens supports larger or equal sensor size to prevent vignetting |
| Image Circle | Diameter of light projected onto sensor | Choose lenses with ≥1.2x sensor diagonal for optimal coverage |
| Mount Type | C-Mount, CS-Mount, F-Mount, S-Mount (M12) compatibility | C-Mount remains industry standard; CS-Mount offers cost savings for smaller sensors |
TOWIN Lens Tip: Our HR series lenses support a maximum 1.1-inch sensor with an image circle diameter of up to 28mm, suitable for 8-20 megapixel area scan cameras.
2. Focal Length, Working Distance, and Field of View (FOV)
Focal Length Formula: Focal Length F = (Working Distance WD × Sensor Size) ÷ Field of View FOV
Working Distance (WD): The distance from the front of the lens to the measured object
- Short Working Distance (10-50mm): Macro lenses, suitable for small component inspection
- Medium Working Distance (50-500mm): Standard industrial application scenarios
- Long Working Distance (>500mm): Robots, assembly lines with limited space
Field of View (FOV): The area captureable by the camera; to ensure motion control flexibility, select an FOV 10-20% larger than the target object
3. Resolution and Modulation Transfer Function (MTF) Performance
- Lens Resolution: Must match or exceed camera resolution (pixels)
- 2026 Trend: 16-50 megapixel lenses are widely used in high-precision manufacturing inspection
- Modulation Transfer Function (MTF): Measures contrast retention capability at different spatial frequencies
- Core Target: Critical applications require MTF ≥ 0.5 at the Nyquist frequency
- Pixel Size Matching: Lenses should resolve details smaller than the camera’s pixel pitch
4. Aperture (f/#) and Depth of Field (DoF)
| Aperture Setting | Pros | Cons | Best Applications |
| Large Aperture (f/1.2-f/2.8) | More light, better low-light performance | Shallow DoF, less depth for focus | High-speed inspection, low-light environments |
| Medium Aperture (f/4-f/8) | Balanced light intake and DoF | – | General-purpose machine vision |
| Small Aperture (f/11-f/16) | Maximum DoF, sharp focus across range | Less light, may require longer exposure | 3D inspection, varying object heights |
Depth of Field Formula: DoF ≈ 2 × N × C × (f²)/(S² × WD), where N = aperture value, C = circle of confusion diameter, f = focal length, S = sensor size, WD = working distance
Types of Industrial Lenses
As a core component of machine vision systems, industrial lenses come in various types and can be classified based on multiple dimensions such as functional characteristics, application scenarios, optical design, and interface type:
1. Classification by Function and Focal Length
| Lens Type | Core Features | Typical Application Scenarios |
| Fixed-Focus Lens (FA Lens) | Fixed focal length, robust structure, low cost, stable imaging | Fixed-position inspection on production lines, surface defect identification, barcode scanning |
| Zoom/Variable Magnification Lens | Adjustable focal length, enables field-of-view (FOV) adjustment without moving the camera/object | Multi-spec product inspection, dynamic FOV adjustment, remote monitoring |
| Telecentric Lens | Chief rays parallel to the optical axis, no parallax, low distortion | High-precision dimensional measurement, stepped object inspection, 3D stacking detection |
| Macro/Micro Lens | High magnification (up to 10:1 or above), clear presentation of fine details | Chip inspection, PCB fine examination, micro-component measurement |
| Liquid Lens | No mechanical movement, rapid focal length adjustment via voltage control | High-speed focusing, multi-depth-of-field inspection, dynamic production lines |
Telecentric Lens Subtypes:
- Object-Side Telecentric: Object position changes do not affect magnification, suitable for objects with height variations
- Image-Side Telecentric: Sensor position changes do not affect imaging, suitable for scenarios requiring high focusing accuracy
- Double-Sided Telecentric: Combines advantages of both object-side and image-side, offering the highest precision, suitable for micrometer-level measurement
2. Classification by Application Scenario
| Lens Type | Special Design | Applicable Fields |
| Line Scan Lens | Long strip-shaped FOV, high resolution, compatible with line scan cameras | Web inspection (e.g., films, paper), large-format object scanning |
| Polarized Lens | Eliminates glare, enhances image contrast | Metal surface inspection, glass product examination, LCD panel testing |
| UV/IR Lens | Optimized for specific wavelengths, strong penetration capability | Fluorescence detection, semiconductor wafer inspection, thermal imaging temperature measurement |
| Fisheye/Wide-Angle Lens | Ultra-large FOV (180°+), compact size | Panoramic monitoring, robot navigation, confined space inspection |
| Long-Focus Lens | Long working distance, high magnification | Long-distance inspection, hazardous area monitoring, large equipment examination |
3. Classification by Optical Interface
| Interface Type | Flange Focal Distance | Features | Applications |
| C-Mount | 17.526mm | Most widely used, threaded connection, compatible with most industrial cameras | General machine vision systems |
| CS-Mount | 12.526mm | Variant of C-mount, smaller size, lower cost | Miniaturized devices, cost-effective systems |
| M12-Mount | 6.5mm | Miniaturized design, fine threads, lightweight | Embedded vision systems, smart cameras |
| M42/M52-Mount | 45.5mm/55mm | Large aperture, high light transmittance, suitable for high-resolution imaging | Research-grade inspection, high-precision measurement systems |
| F-Mount | 46.5mm | Bayonet connection, easy assembly and disassembly, compatible with DSLR industrial cameras | High-end imaging systems, special optical requirements |
4. Classification by Imaging Plane and Scanning Method
- Area Scan Lenses: Compatible with area scan cameras, capturing 2D images at once, suitable for static object inspection
- Line Scan Lenses: Compatible with line scan cameras, imaging via progressive scanning, suitable for high-speed moving object inspection
- Relay Lenses: Extend optical paths and adjust imaging ratios, suitable for complex optical system integration
5. Classification by Aperture Control
- Fixed Aperture: Simple structure, low cost, suitable for stable lighting environments
- Manual Aperture: Manually adjust light transmission, suitable for scenarios with minimal lighting changes
- Auto Aperture: Automatically adjusted via motor/voltage, suitable for dynamic lighting environments
6. Special Function Lenses
- Tilt-Shift Lenses: Optical axis can be tilted and shifted to correct perspective distortion, suitable for 3D object inspection
- Fiber Optic Lenses: Cooperate with optical fibers to transmit and shape light signals, suitable for narrow space inspection
- High-Resolution Lenses: Up to 10+ megapixels, suitable for precision measurement and microscopic imaging
- Low-Distortion Lenses: Distortion rate < 0.1%, suitable for high-precision measurement and metrology systems
Selection Recommendations
- Prioritize double-sided telecentric lenses for measurement applications to ensure precision
- Recommend liquid lenses or auto-zoom lenses for dynamic production lines to improve efficiency
- Must select macro/microscopic lenses for small object inspection to ensure clear details
- Consider polarizing lenses for metal/glass surface inspection to eliminate reflection interference
- Prioritize fixed-focus FA lenses for cost-sensitive projects due to high cost-effectiveness
6mm Low Distortion Industrial Lens
2026 Industrial Lens Selection Process
Core Principle: Centered on “inspection precision, field of view, and working distance”, follow a systematic process of “requirement definition → parameter matching → verification and implementation”, and balance performance with cost by integrating technical trends (liquid lenses, telecentric popularization).
1. Core Selection Process
- Clarify Core Requirements: Determine inspection targets (size/material), precision requirements (micrometer/mm level), speed cycle, installation space (working distance, protection level), and budget range.
- Match Camera Parameters: Confirm camera sensor size (lens image circle ≥ sensor diagonal), resolution (lens resolution ≥ camera pixel density), and interface type (prioritize C/M12 interfaces).
- Calculate Key Parameters: Quickly calculate via core formulas (FOV = Sensor Size × WD ÷ Focal Length; Pixel Size = FOV ÷ Camera Resolution; Magnification = Sensor Size ÷ FOV).
- Select Lens Type: Match by scenario — double-sided telecentric for measurement, fixed-focus FA for static inspection, motorized zoom for multi-spec products, macro for small objects, liquid lenses for high-speed lines, and line scan for large formats.
- Verify Compatibility and Environmental Adaptation: Confirm interface/flange distance matching, evaluate environmental requirements (temperature, humidity, vibration, dust), and select corresponding protective/wide-temperature designs.
- On-Site Test Verification: Simulate actual environments to verify imaging quality, precision error, and stability, ensuring compliance with production requirements.
2. Core Calculation Formulas
- Pixel Size (mm/px) = FOV Range ÷ Camera Resolution (critical for precision; smaller = more accurate)
- Focal Length (mm) = Working Distance × Sensor Size ÷ FOV Range
- Magnification = Sensor Size ÷ FOV Range = Focal Length ÷ Working Distance
- Depth of Field (mm) ≈ 2×N×(f/#)×PE²×(WD/f)² (N = object-side refractive index, f/# = aperture value)
3. Common Misunderstandings and Pitfalls to Avoid
- Overpursuing High Parameters: Performance meeting requirements +10% is sufficient to avoid cost waste
- Ignoring Sensor Matching: Vignetting is likely; always verify image circle and sensor compatibility
- Underestimating Environmental Impact: Prioritize protective/wide-temperature designs for harsh environments to avoid shortened service life
- Interface Mismatch: Confirm flange distance in advance (e.g., C-mount 17.526mm) to avoid installation failure
4. Scenario-Lens Quick Matching Table
| Application Scenarios | Recommended Lens Type | Core Requirements |
| High-precision Dimensional Measurement | Dual-sided Telecentric | Distortion < 0.1%, Low Error |
| General Appearance Defect Inspection | Fixed-focus FA Lens | Low Distortion, High Light Transmittance |
| Multi-spec Product Inspection | Motorized Zoom Lens | Auto Focus, Stable Zoom Ratio |
| High-speed Production Line | Liquid Lens | Millisecond-level Focusing, High Frame Rate |
| Large-format/Roll Material Inspection | Line Scan Lens | Compatible with Line Scan Cameras, Long Strip Field of View |
Customized Lens Selection Solutions for Different Industry Scenarios
1. Precision Inspection Lens Selection for the Semiconductor Industry
- Semiconductor Industry Precision Inspection: Micrometer-level inspection targets (wafer, chip packaging) require ultra-high precision; cleanroom compatibility (dust-free, low-vibration) and UV/IR damage prevention are mandatory.
- Key Requirements: Resolution ≥ 200 lp/mm, distortion < 0.05%, low UV/IR damage, high anti-interference.
- Recommended Lenses: Double-sided telecentric (dimensional measurement), high-magnification macro/microscopic (chip details), deep UV-compatible (wafer defects).
- Customization: Anti-static/anti-particle surface treatment, IP54+ for cleanrooms, low-fluorescence materials to avoid reflection interference.
2. Lens Selection for NEV Three-Electric System Inspection
- NEV Three-Electric System Inspection: Diverse scenarios (battery, motor, EC) with workshop environments (vibration, dust) and wide temperature needs (-20℃~+85℃).
- Key Requirements: High stability, wide temperature adaptability, large FOV or high precision as needed.
- Recommended Lenses: Line scan (battery pole pieces), double-sided telecentric (battery tabs), anti-vibration fixed-focus FA (motor parts), high-resolution (EC PCB solders).
- Customization: Reinforced lens barrel (anti-vibration), sealed structure (dust), wide-temperature optical materials for battery inspection.
3. Appearance Inspection Lens Selection Guide for the Consumer Electronics Industry
- Consumer Electronics Appearance Inspection: Rapid product iteration, diverse specs (phone, headphone), needs for scratch/color difference inspection; high speed and anti-reflection for metal/glass parts.
- Key Requirements: Low distortion (<0.5%), high contrast, fast focusing, multi-spec adaptability.
- Recommended Lenses: Fixed-focus FA (mass production), motorized zoom (multi-spec), polarizing (anti-reflection), liquid lenses (high-speed lines).
- Customization: Custom focal length, compact design for small spaces, adjustable aperture for varying lighting.
4. Key Lens Selection Points for Emerging Medical and Agricultural Scenarios
- Emerging Medical & Agricultural Scenarios: Medical needs high precision and biocompatibility; agricultural requires outdoor adaptability (temperature variation, dust) and spectral inspection capability.
- Key Requirements: Medical – high resolution, biocompatible materials; Agricultural – weather resistance, special spectral adaptability (e.g., near-infrared).
- Recommended Lenses: Medical – high-magnification microscopic (pathology), low-distortion endoscope; Agricultural – near-infrared (pest detection), wide-angle (farm monitoring), macro (seed screening).
- Customization: Medical – medical-grade stainless steel (sterilization); Agricultural – anti-fog/anti-corrosion (-30℃~+60℃), customized spectral transmittance.

M12 fixed-focus CCTV industrial lenses
Analysis of 7 Best TOWIN Industrial Lenses
1. 50mm FA Lens (Model: C5011028m20)
Core Parameters
- Interface Type: C-Mount
- Focal Length: 50mm
- Image Circle Compatibility: 2/3″ (compatible with 1″ small sensor)
- Resolution: 10MP+
- Distortion Rate: <0.1%
- Aperture Range: F2.8~F16
- Minimum Working Distance (WD): 150mm
Core Advantages
- Medium focal length + low distortion, strong imaging stability, and outstanding cost-effectiveness;
- Light transmittance ≥ 92%, ensuring clear imaging in low-light environments;
- Sturdy structure with anti-vibration design for workshop assembly line environments.
Application Scenarios & Industry Matching
- Consumer Electronics: Appearance defect inspection (scratches, burrs) of mobile phone middle frames and home appliance accessories;
- New Energy Vehicles: Motor housing dimension verification, electronic control box assembly gap inspection;
- General Manufacturing: Batch inspection of standardized components (e.g., screws, gaskets).
Selection Points
- Suitable for “medium distance + medium FOV + high-precision appearance inspection”; pixel size can be as low as 0.02mm/px (with 5-megapixel camera);
- Not recommended for narrow-space installation (lens length approx. 80mm).

50mm-C-mount Machine Vision FA lens
2. 35mm Industrial Lenses (Model: C3511028m20)
Core Parameters
- Interface Type: C-Mount
- Focal Length: 35mm
- Image Circle Compatibility: 2/3″
- Resolution: 10MP+
- Distortion Rate: <0.15%
- Aperture Range: F2.8~F16
- Minimum Working Distance (WD): 100mm
Core Advantages
- Moderate focal length, balancing FOV and magnification;
- High edge imaging clarity without vignetting;
- Controllable cost, suitable for mass production line deployment.
Application Scenarios & Industry Matching
- New Energy Vehicles: Battery tab dimension measurement, motor winding arrangement inspection;
- Consumer Electronics: PCB surface component solder joint integrity inspection;
- General Manufacturing: Appearance inspection of precision mechanical parts (e.g., gears, bearings).
Selection Points
- Suitable for “medium distance + small-medium FOV + both measurement and inspection”; 0.01mm/px pixel size achievable with 20-megapixel camera;
- Prioritize for static inspection scenarios (production line cycle ≤ 300 units/minute).
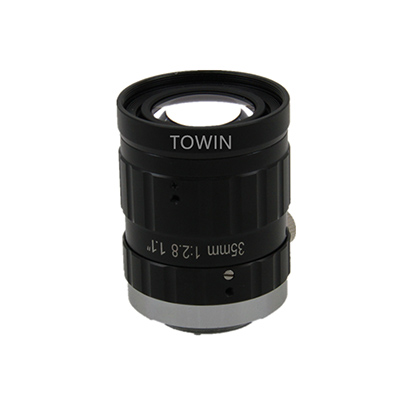

35mm C mount industrial lenses
3. 25mm C-FA Lens (Model: C2511028m20)
Core Parameters
- Interface Type: C-Mount
- Focal Length: 25mm
- Image Circle Compatibility: 2/3″
- Resolution: 10MP+
- Distortion Rate: <0.2%
- Aperture Range: F2.8~F16
- Minimum Working Distance (WD): 80mm
Core Advantages
- Short focal length + large FOV, suitable for simultaneous inspection of multiple parts at close range;
- Short focusing stroke, easy operation, and high debugging efficiency;
- Temperature range: -10℃~+60℃, adapting to most workshop environments.
Application Scenarios & Industry Matching
- Consumer Electronics: Batch appearance inspection of headphone casings and charger housings;
- New Energy Vehicles: Battery module heat sink assembly inspection, charging pile interface appearance;
- Medical Industry: Defect screening of medical plastic accessories (e.g., syringe housings).
Selection Points
- Suitable for “close range + large FOV + batch inspection”; FOV up to 80mm×60mm at 100mm WD (with 2/3″ sensor);
- For measurement scenarios: Note that distortion rate is slightly higher than 50mm/35mm lenses; prioritize for precision requirements > 0.05mm.
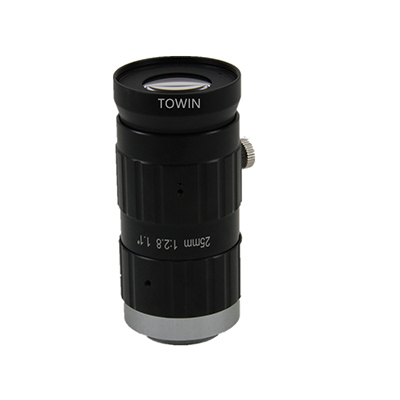

25mm C mount industrial lenses
4. 16mm 20MP MV Industrial Lenses (Model: C1611028m20)
Core Parameters
- Interface Type: C-Mount
- Focal Length: 16mm
- Image Circle Compatibility: 1″ (compatible with 2/3″)
- Resolution: 20MP (ultra-high pixel compatibility)
- Distortion Rate: <0.2%
- Aperture Range: F2.8~F16
- Minimum Working Distance (WD): 50mm
Core Advantages
- 20-megapixel resolution with strong detail capture capability;
- 1″ large image circle, compatible with high-pixel large sensor cameras;
- Low dispersion design for high color reproduction (suitable for color difference inspection).
Application Scenarios & Industry Matching
- Semiconductor Industry: Chip packaging pin defect inspection, wafer edge scratch identification;
- Consumer Electronics: Mobile phone screen glass scratches (≤0.01mm), camera module detail inspection;
- New Energy Vehicles: High-precision inspection of high-density PCB solder joints (avoiding cold solder and bridge defects).
Selection Points
- Suitable for “high-precision detail inspection + high-pixel camera matching”; pixel size can be as low as 0.005mm/px (with 20-megapixel camera);
- Note: High resolution requires high lighting; recommend using ring light sources.
5. 12mm FA 1″ Industrial Lenses (Model: C1211028m20)
Core Parameters
- Interface Type: C-Mount
- Focal Length: 12mm
- Image Circle Compatibility: 1″ (large sensor compatible)
- Resolution: 15MP+
- Distortion Rate: <0.3%
- Aperture Range: F2.8~F16
- Minimum Working Distance (WD): 30mm
Core Advantages
- 1″ large image circle + short focal length for ultra-large FOV imaging;
- Compact lens size (approx. 65mm length), suitable for narrow-space installation;
- Wide-temperature design (-20℃~+70℃), adapting to harsh environments.
Application Scenarios & Industry Matching
- New Energy Vehicles: Battery pack overall dimension inspection, power battery module panoramic assembly inspection;
- Consumer Electronics: Tablet PC housing panoramic appearance inspection, TV frame joint gap inspection;
- Agricultural Scenarios: Large-area seed screening (batch inspection of seed shape and damage).
Selection Points
- Suitable for “large format + close-range inspection”; FOV up to 100mm×75mm at 50mm WD (with 1″ sensor);
- For measurement scenarios: Control precision expectations (distortion rate < 0.3%, suitable for precision requirements < 0.1mm).
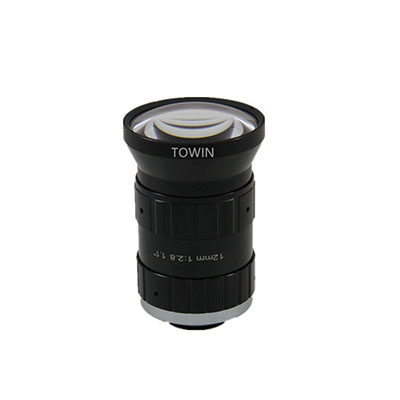

20MP 12mm low distorton C-mount FA lens
6. Wide-Angle Industrial Lenses (Model: C0811014m20)
Core Parameters
- Interface Type: C-Mount
- Focal Length: 8mm
- Image Circle Compatibility: 2/3″
- Resolution: 8MP+
- Distortion Rate: <0.5% (optimal for wide-angle lenses)
- Aperture Range: F1.4~F16
- Minimum Working Distance (WD): 15mm
Core Advantages
- Ultra-wide-angle design with FOV ≥ 90°, full panoramic coverage without blind spots;
- Large aperture (F1.4) for clear imaging in low-light/narrow spaces;
- Anti-fog coating, suitable for humid environments.
Application Scenarios & Industry Matching
- Industrial Robots: Narrow-space navigation (e.g., internal equipment inspection);
- Agricultural Scenarios: Farmland panoramic monitoring, greenhouse crop growth status observation;
- General Manufacturing: Internal defect inspection of large equipment chambers (e.g., storage tanks, pipelines).
Selection Points
- Suitable for “panoramic coverage + narrow space + dynamic monitoring”; not recommended for high-precision measurement (relatively high distortion rate);
- Reserve space at the front of the lens during installation (minimum WD only 15mm).
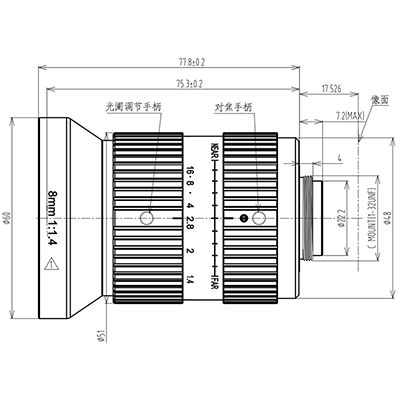
1.1″ C-Mount 8mm Low distortion Wide-angle lens
7. C-Mount Industrial Lenses (Model: C0611018m20)
Core Parameters
- Interface Type: C-Mount
- Focal Length: 6mm
- Image Circle Compatibility: 2/3″
- Resolution: 8MP+
- Distortion Rate: <0.6%
- Aperture Range: F1.8~F16
- Minimum Working Distance (WD): 10mm
Core Advantages
- Ultra-wide angle + ultra-short WD for close-range large FOV coverage;
- Lightweight (only 35g), suitable for embedded device installation;
- Low cost, suitable for economical inspection systems.
Application Scenarios & Industry Matching
- Consumer Electronics: Batch inspection of small components (e.g., headphone earbuds, mobile phone SIM card slots);
- Medical Industry: Appearance screening of small medical devices (e.g., blood collection needles);
- General Manufacturing: Panoramic inspection of micro-sized parts (e.g., micro screws, gaskets).
Selection Points
- Suitable for “ultra-close range + small-sized part batch inspection”; FOV up to 50mm×40mm at 20mm WD (with 2/3″ sensor);
- Supplemental lighting required in low-light environments (large aperture improves light intake but reduces DoF).
7-Lens Quick Selection Matching Table
| Lens Model | Core Adaptable Scenarios | Priority Industries | Precautions |
| C5011028m20 (50mm) | Medium-distance + High-precision Appearance Inspection | Consumer Electronics, New Energy | Not suitable for installation in confined spaces |
| C3511028m20 (35mm) | Medium Field of View + Balanced Measurement & Inspection | New Energy, General Manufacturing | Prefer static inspection scenarios; test frame rate for high-speed applications |
| C2511028m20 (25mm) | Short-distance + Large Field of View + Batch Inspection | Consumer Electronics, Medical Industry | Exercise caution for high-precision measurement requirements |
| C1611028m20 (16mm) | High-pixel + Precision Detail Inspection | Semiconductor, Consumer Electronics | Must be paired with high-pixel cameras and high-quality light sources |
| C1211028m20 (12mm) | Large Format + Large Sensor Compatibility | New Energy, Agriculture | Ideal for installation in confined spaces |
| C0811014m20 (8mm) | Panoramic Coverage + Confined Space Navigation/Inspection | Industrial Robotics, Agriculture | Not suitable for high-precision measurement |
| C0611018m20 (6mm) | Ultra-short Distance + Batch Inspection of Micro-components | Consumer Electronics, Medical Industry | Supplementary lighting required in low-light environments |
FAQs
Q1: How to precisely match the lens resolution with the camera’s pixel count?
A1: Core principle: Lens resolution ≥ camera’s Nyquist frequency requirement (MTF ≥ 0.5 at this frequency). There’s no need to blindly pursue ultra-high resolution; performance meeting requirements +10% is sufficient to avoid cost waste.
Q2: How to distinguish application scenarios for object-side, image-side, and double-sided telecentric lenses?
A2: Object-side telecentric lenses are suitable for objects with height variations; image-side telecentric lenses for scenarios with potential sensor position changes or high focusing accuracy requirements; double-sided telecentric lenses offer the highest precision for micrometer-level measurement but are costly, making them unnecessary for non-high-precision needs.
Q3: What are effective solutions for insufficient working distance?
A3: Solutions include selecting short-focal-length lenses, using relay lenses, or adopting macro lenses. Note that short-focal-length lenses may have higher distortion rates; verify if they meet precision requirements.
Q4: What are top lens selection indicators for harsh industrial settings?
A4: Focus on environmental adaptability and protective performance. Choose lenses with wide-temperature designs, anti-vibration reinforcement, and appropriate protection levels (e.g., IP54+), and prioritize aluminum alloy or stainless steel lens barrels.
Q5: How to maintain lenses during use to ensure long-term imaging stability?
A5: Clean lenses standardizedly, install and fix interfaces correctly, add protective covers in harsh environments, calibrate every 3-6 months for high-precision scenarios, and store in a dry, cool, and vibration-free environment when not in use.

25mm-Low Distortion Telecentric Lens
Conclusion
In 2026, the selection of machine vision lenses has shifted from “parameter stacking” to “precision requirement matching”, with high pixelation, customization, and environmental adaptability as core directions. This guide establishes a full-link selection system of “requirement definition → parameter matching → scenario adaptation → cost balance”. The core logic is to base selection on inspection precision, FOV, and working distance, match lenses to scenarios, and ensure imaging stability through on-site testing to achieve optimal balance between performance and cost.
In the future, technologies such as liquid lenses and telecentric popularization will further expand application boundaries. When selecting lenses, enterprises should not only refer to this guide but also focus on manufacturers’ customization capabilities and after-sales services, choose products with proven reliability based on their scenarios and budgets, and conduct joint customized development when necessary to lay an optical foundation for the stable operation of machine vision systems.