IR Correction Impact on Night Vision Performance
Top 5 Best 1/1.8-inch M12 lenses
01/06/2026
12mm 1/3″ CCTV M12 Pinhole lens
01/08/2026Table of Contents
- Introduction
- What is Infrared Correction? Core Principles and Technical Methods
- Key Impact Dimensions of Infrared Calibration on Night Vision Performance
- Application Cases: Performance of Infrared Correction in Actual Night Vision Scenarios
- Analysis of 5 Best Infrared Corrected Lenses from Towin
- FAQs
- Conclusion
Introduction
In key fields like security monitoring, intelligent transportation, industrial inspection and military reconnaissance, night vision performance directly determines equipment’s target recognition capability and data reliability in low-light or no-visible-light environments. Due to scarce natural light at night, imaging systems rely on infrared band (780nm~1mm) radiation, but refractive index differences between infrared and visible light, as well as optical component defects, easily cause aberrations, noise and blurred images. IR Correction tech, via hardware-software synergy, resolves night vision issues, breaking bottlenecks as core support.
What is IR Correction? Core Principles and Technical Methods
IR Correction refers to technologies that eliminate/compensate for errors, distortions, and noise in optical systems, imaging equipment, or spectral data targeting the infrared band (780nm~1mm) through hardware design, software algorithms, or system calibration to obtain accurate and reliable infrared signals/images. Its core goal is to restore the true infrared radiation or optical characteristics of the target.

IR corrected 1.17mm M12 Fisheye CCTV lens
1. Classification of Core Principles
- Non-Uniformity Correction (NUC): IRFPA tech compensates pixel responsivity/offset, removes fixed-pattern noise, and uses linear models for uniform output.
- Optical Aberration Correction: Addresses chromatic aberration, spherical aberration, and other aberrations caused by the difference in refractive index between infrared and visible light. Based on geometric/wave optics principles, it compensates for wavelength-dependent aberrations through optical design to ensure precise focusing.
- Radiometric Calibration: Links detector output to true target brightness/temperature, removes nonlinearity and interference, enabling precise measurements.
- Spectral Data Correction: Uses signal processing and chemometrics to cut baseline drift, scattering, noise, and boosts analysis accuracy.
2. Mainstream Technical Methods
- Imaging Calibration and Correction: Single-point correction (calculates offset compensation), two-point correction (high and low-temperature blackbody calibration, compensates for gain and offset, mainstream standard method), multi-point correction (multi-temperature calibration, fits nonlinear curves, suitable for high-precision scenarios).
- Optical Aberration Correction: Hardware employs advanced optics; software utilizes smart algorithms for precise infrared imaging and analysis.
- Spectral Preprocessing and Correction: Baseline correction (derivative, wavelet transform), scattering correction (MSC, SNV), noise suppression (moving average, Fourier filtering).
- Adaptive Correction: Scene-based non-uniformity correction (temporal high-pass filtering, constant statistics method), environment-adaptive correction (temperature compensation, atmospheric correction).
3. Core Applications
Infrared thermal imaging (industrial temperature measurement, security), IR lens manufacturing (day-night dual-use), remote sensing detection (surface temperature acquisition), infrared spectral analysis of materials, military night vision/guidance systems.
Key Impact Dimensions of Infrared Calibration on Night Vision Performance
Infrared Calibration is a core technology for optimizing the performance of night vision optical systems. By compensating for optical deviations in the infrared band, it directly influences the imaging quality, environmental adaptability, and target recognition capability of night vision devices. Six key dimensions, blending theory and practice, analyze impact via a table highlighting core mechanisms:
| Impact Dimension | Core Impact | Technical Principle | TOWIN Application Case |
| Image Sharpness & Detail Restoration | Eliminates blur/ghosting, enhances edge sharpness and detail | Aligns IR & visible light via special optics/algorithms | NV Series: Dual-band calibration, clear imaging at 0.01lux |
| Contrast & Dynamic Range | Reduces foggy effect, improves target-background separation | Suppresses stray light, optimizes IR transmittance curve | IR-Cal Series: IR transmittance >95%, dynamic range +30% |
| Color Accuracy (Color Night Vision) | Avoids color cast, restores true target color | Balances spectral response via calibration algorithms/filters | ColorNight: Color restoration error ≤5%, suitable for color-sensitive scenarios |
| Field of View (FOV) Consistency | Ensures IR-visible FOV consistency, no edge distortion | Geometric calibration aligns multi-band refraction paths | Wide-angle lens: 120° FOV, deviation ≤1% |
| Environmental Adaptability | Improves low-temp stability, suppresses glare | Temperature compensation, IR cut filter + anti-reflection coating | Industrial-grade: -40℃~+60℃ workable, glare suppression 85% |
| Target Recognition Distance & Accuracy | Extends recognition distance, reduces false rate | Optimizes MTF, enhances IR light-gathering efficiency + AI integration | Long-range lens: 1000m recognition, 98% accuracy for humans/vehicles |
Application Cases: Performance of IR Correction in Actual Night Vision Scenarios
The value of IR Correction technology is ultimately reflected in specific scenarios. By solving core pain points in different night vision environments, it demonstrates significant performance improvements. The following are the actual performances in typical application scenarios:
1. Security Monitoring (Outdoor Nighttime No-Supplementary Light Scenarios)
- Scenario Requirements: For outdoor areas such as residential districts and parks without streetlights or supplementary light equipment at night, it is necessary to clearly identify human faces, vehicle outlines, and movement trajectories, avoiding image noise and target blurring caused by low light.
- Role of IR Correction: Adopting infrared corrected lenses (e.g., Towin D14331112516A5M-1) to eliminate the focusing deviation between infrared light and visible light through optical aberration correction, achieving “day-night parfocality”; combining with F1.6 large aperture design to increase low-light light intake, and suppressing fixed noise with non-uniformity correction.
- Actual Performance: In nighttime no-supplementary light environments, the image signal-to-noise ratio is improved by more than 30%. Clear facial recognition within 15m, distortion-free license plates, and no trailing for moving targets. It solves the pain point of traditional uncorrected lenses that “are clear during the day but blurred at night.”
2. Traffic ITS (Nighttime Road Monitoring Scenarios)
- Scenario Requirements: For nighttime monitoring of highways and urban main roads, it is necessary to accurately capture long-distance vehicle license plates and models, cope with interference such as vehicle light glare, road reflection, and atmospheric scattering, and ensure the accuracy of traffic violation identification and flow statistics.
- Role of IR Correction: Long-focus IR corrected lenses (e.g., Towin C167011714A8) compensate for the impact of atmospheric attenuation through radiometric calibration, suppress chromatic aberration and spherical aberration in optical design, enhance low-light sensitivity with F1.4 ultra-large aperture, and ensure no deformation of long-distance targets with low distortion (6.1%).
- Actual Performance: The recognition rate of vehicle license plates within 50 meters at night reaches over 95%. Adjacent vehicles can still be distinguished under vehicle light glare. Image contrast stays stable in -10℃, haze, ensuring 24/7 traffic monitoring without interruption.
3. Industrial Inspection (Nighttime Equipment Temperature Measurement Scenarios)
- Scenario Requirements: For nighttime inspection of power substations and chemical plant areas, infrared thermal imaging is required to detect abnormal heating of equipment. The temperature measurement error is required to be ≤±2℃ to avoid misjudgment caused by infrared signal distortion.
- Role of IR Correction: IR corrected lenses (e.g., Towin C281212M2) combine radiometric calibration technology to establish a quantitative relationship between detector output and true temperature, eliminating environmental temperature interference and the lens’s own thermal noise; manual focusing and aperture design adapt to the needs of short-distance equipment detection.
- Actual Performance: The temperature measurement error of equipment such as power connectors and pipeline valves at night is controlled within ±1.5℃. Clear heating point outlines, no false hot spots, enabling precise fault location and reducing night inspection risks.
4. Indoor Short-Distance Monitoring (Supermarkets, Warehouses Scenarios)
- Scenario Requirements: For indoor low-light environments (such as underground warehouses and supermarket nighttime duty), it is necessary to cover a large area while ensuring clear details of short-distance goods and personnel. The lens needs to be compact and easy to install with no obvious distortion.
- Role of IR Correction: Ultra-wide-angle IR corrected lenses (e.g., Towin CCL118032MPCS) eliminate the scattering interference of indoor infrared supplementary lights through spectral data correction, cover the entire scene with a 153° large field of view, and avoid edge target stretching with low distortion design.
- Actual Performance: A single lens can fully cover a 50㎡ indoor space. Goods labels can be identified within 3 meters, human movement trajectories have no distortion, and the lens is compact (adapting to CS mount) and flexible to install, meeting the needs of intensive indoor monitoring.
16mm IR-corrected low-distortion CCTV lens
Analysis of 5 Best IR Corrected Lenses from Towin
Based on 5 core IR corrected lenses provided on Towin’s official website, combined with their technical parameters and night vision performance adaptability, the targeted analysis is as follows:
1. D14331112516A5M-1: Zoom IR Corrected Lens for Versatile Scene Adaptation
Core Parameters: 5MP, 3.3-11mm zoom focal length, F1.6 aperture, Φ14 mounting, DC auto iris, IR corrected, distortion -59%~-3%, minimum focusing distance 0.5m
IR Correction Related Advantages:
- Zoom design + IR correction: 3.3mm wide angle (115° horizontal field of view) adapts to large-area monitoring, 11mm telephoto adapts to medium and long-distance targets, and IR Correction ensures consistent day and night focus during zooming without defocusing;
- DC auto iris: Automatically adjusts light intake according to nighttime light intensity, combined with F1.6 large aperture, ensuring sufficient light intake in low-light environments and reducing noise;
- Stepper motor focusing/zooming: Precise adjustment, suitable for security scenarios that require dynamic adjustment of monitoring range (such as park perimeters, shopping mall atriums).
Night Vision Performance Adaptable Scenarios: Outdoor medium and short-distance flexible monitoring, multi-target switching scenarios. Targets within 10-20 meters can be clearly identified at night without supplementary light.
5 Megapixel IR corrected CCTV lens
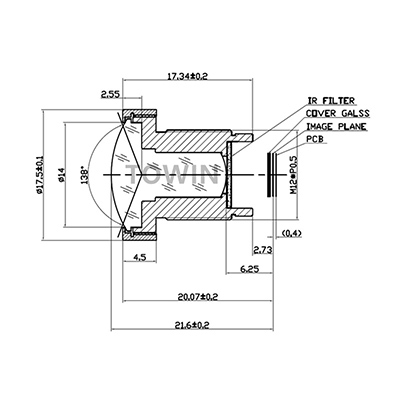
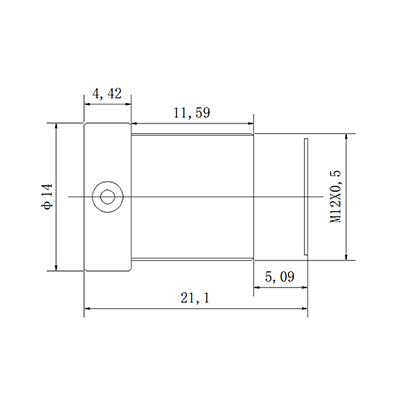
2. CCL12516MPR2: Low Distortion Short-Distance Precision Monitoring Lens
Core Parameters: 5MP, 16mm fixed focal length, F2.0 aperture, M12×0.5 mounting, fixed aperture, IR corrected, distortion <-0.3%, minimum focusing distance 0.2m
IR Correction Related Advantages:
- Ultra-low distortion (<-0.3%): IR Correction combined with optical design avoids nighttime target deformation, especially suitable for scenarios that require precise identification of target outlines such as entrances and exits, elevator lobbies;
- Short-distance focusing (0.2m): IR correction ensures clear infrared imaging at short distances without blurring, adapting to indoor short-distance monitoring (such as offices, warehouse shelves);
- Compact size (Φ14×15.8mm): M12 S-mount installation, adapting to small security cameras, easy to install.
Night Vision Performance Adaptable Scenarios: Indoor and outdoor short-distance fixed monitoring, target outline precise identification scenarios. Details within 2-15 meters can be clearly captured at night.
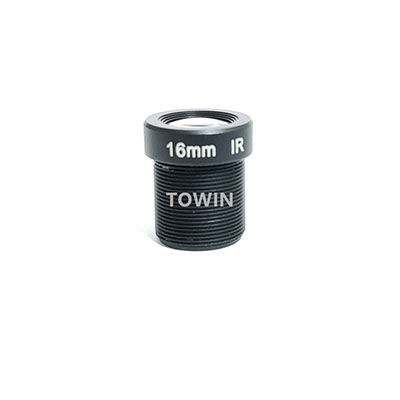

IR-corrected-Low-distortion-CCTV-16mm-M12-lens
3. CCL118032MPCS: Ultra-Wide-Angle High-Resolution Panoramic Monitoring Lens
Core Parameters: 12MP, 3.2mm fixed focal length, F2.0 aperture, CS mounting, fixed aperture, IR corrected, distortion <-64%, 153° diagonal field of view
IR Correction Related Advantages:
- 12MP high resolution + IR correction: Retains rich details in large-area nighttime scenarios without noise, suitable for panoramic monitoring needs such as parking lots and squares;
- Ultra-wide angle (153°) + aberration correction: IR Correction eliminates edge aberrations of ultra-wide-angle lenses, ensuring no blurring or stretching at the edge of nighttime images and consistent clarity across the entire field of view;
- Adapts to 1/1.8″ large sensor: Larger sensor combined with IR correction improves low-light photosensitivity, ensuring uniform image brightness in nighttime no-supplementary light environments.
Night Vision Performance Adaptable Scenarios: Large-scale indoor and outdoor panoramic monitoring, large-area target coverage scenarios. Panoramic details within 30 meters can be clearly presented at night.
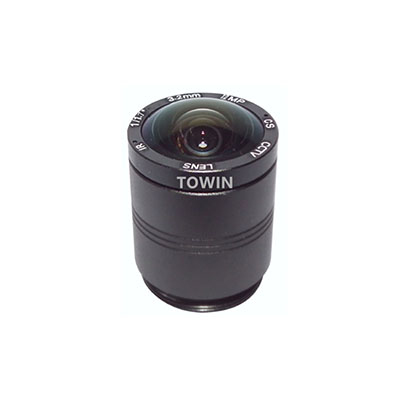

IR-corrected-CS-mount-lens
4. C281212M2: Short-Distance Industrial-Grade Night Vision Inspection Lens
Core Parameters: 2MP, 2.8-12mm zoom focal length, F1.6 aperture, C mounting, manual aperture, IR corrected, minimum focusing distance 0.1m
IR Correction Related Advantages:
- Ultra-short-distance focusing (0.1m): IR correction ensures no distortion or blurring of infrared imaging at short distances, suitable for short-distance inspection of industrial equipment (such as circuit boards, pipeline interfaces);
- Manual aperture/focusing: Light intake can be manually adjusted according to nighttime inspection environments, adapting to complex industrial scenarios (such as high-temperature, high-dust environments);
- 1/2″ sensor adaptation: IR Correction is optimized for medium-sized sensors, ensuring stable signal-to-noise ratio in low light and meeting the precision requirements of industrial night vision temperature measurement.
Night Vision Performance Adaptable Scenarios: Industrial equipment nighttime inspection, short-distance fault detection scenarios. Equipment details and temperature abnormalities within 0.1-10 meters can be accurately captured at night.
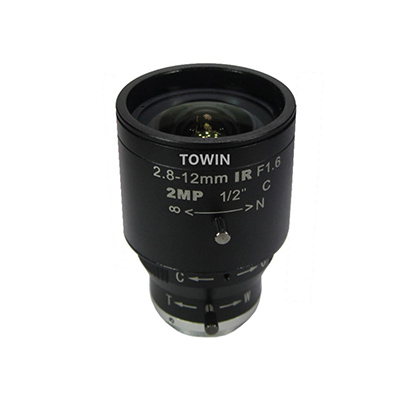

2.8-12mm IR corrected C mount Zoom lens
5. C167011714A8: Traffic-Specific Long-Distance Low-Light Monitoring Lens
Core Parameters: 8MP, 16-70mm long zoom focal length, F1.4 ultra-large aperture, C mounting, DC auto iris, IR corrected, distortion 6.1%, minimum focusing distance 1.5m
IR Correction Related Advantages:
- F1.4 ultra-large aperture + IR correction: Industry-leading light intake in nighttime low-light environments, combined with IR Correction to suppress noise, ensuring clear details of targets within 50 meters without trailing;
- Long zoom (16-70mm): IR Correction ensures no aberrations in long-distance imaging (70mm focal length), suitable for long-distance license plate recognition and road sign capture in traffic roads;
- ITS traffic-specific design: Radiometric calibration + infrared correction resists nighttime vehicle light glare and atmospheric scattering, meeting the 24/7 uninterrupted operation requirements of traffic monitoring.
Night Vision Performance Adaptable Scenarios: Nighttime traffic monitoring of highways and urban main roads, long-distance (10-50 meters) license plate recognition and vehicle tracking scenarios.
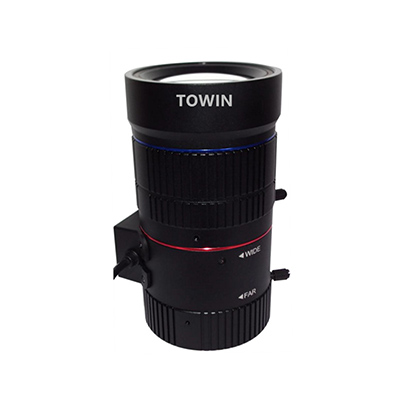

IR corrected C-mount ITS traffic CCTV lens
FAQs
1. What is the core difference between IR corrected lenses and ordinary night vision lenses?
Ordinary night vision lenses only rely on infrared supplementary lights without optimizing infrared optical characteristics, easily causing day-night focus shift, distortion and low-light noise. IR corrected lenses remove infrared-visible aberration gaps for day-night sharpness, reducing noise and distortion, boosting night imaging.
2. What parameters should be prioritized when selecting night vision IR corrected lenses?
Prioritize 4 core parameters: ① Aperture (smaller F-value = more low-light intake, e.g., F1.4 > F1.6); ② IR correction mark (“IR Corrected” for day-night parfocality); ③ Scene-adaptive parameters (wide/telephoto, distortion rate, minimum focusing distance); ④ Resolution (high pixels retain more nighttime details).
3. Will the IR Correction function degrade over time?
No. IR Correction relies on hardware optimization/material selection and factory software calibration, with no easily worn components. As long as optical lenses are intact, the correction effect remains stable long-term without post-maintenance or recalibration.
4. Are IR corrected lenses necessarily clearer than ordinary lenses in low-light environments?
Not necessarily—it depends on parameters like aperture and sensor size. Under identical parameters, IR corrected lenses excel; ordinary ones still blur/distort due to infrared aberration, which it eliminates.
5. Are IR corrected lenses suitable for all night vision scenarios?
They suit most scenarios requiring high imaging quality and recognition rate (e.g., security, traffic, industrial inspection). For temporary, low-quality-demand scenarios, ordinary lenses work, but IR corrected lenses offer better stability and reliability.
Conclusion
By solving core problems such as aberrations, noise, and distortion in the infrared band, IR Correction technology has become a “key link” in improving night vision imaging performance. Its value lies not only in optimizing image quality but also in ensuring the accuracy and reliability of data in low-light environments. From security monitoring to traffic ITS and industrial inspection, IR correction tech offers key support for nighttime operations.