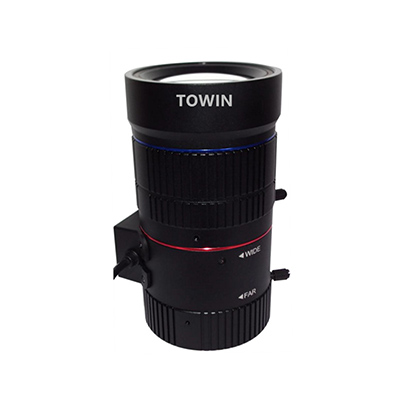
Robotic arm integrated vision system lenses

Industrial automation barcode scanning lens
01/29/2026
IR corrected lenses for 24/7 day/night surveillance
01/31/2026Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Robot Arm Vision System Overview
- Core Role of Lenses in Robot Vision
- Two Lens Mounting Methods for Robot Vision
- Key Parameters of Robot Vision Lenses
- Robot Vision Lens Types & Use Cases
- Robot Arm Lens Selection Process
- Towin Robot Arm Vision System Lenses
- Scenario-Specific Lens Recommendation
- FAQs
- Conclusion
Key Takeaways
- Robot arm vision performance depends on high-quality lenses, which determine image clarity, distortion control, and positioning precision.
- Core lens selection factors: focal length, resolution, distortion (<0.01%~<-0.1% for industrial use), mount type (C-Mount/M12), and mounting method (Eye-in-Hand/Eye-to-Hand).
- Towin’s lenses (8MP~25MP) offer low distortion, compact designs, and multi-scenario adaptation for automation tasks like inspection, assembly, and sorting.
- Scenario-specific recommendations (electronics, automotive, logistics) and global technical support simplify integration.
Introduction
In the era of industrial automation, robot arms have evolved from programmed tools to intelligent collaborators—and their “vision” is the key driver of this transformation. A robot arm’s visual system acts as its “eyes,” enabling tasks like precise component assembly, defect inspection, and dynamic object grasping. Among all components of this system, the lens is the critical link that converts real-world scenes into clear, usable image signals.
For manufacturers and system integrators worldwide, choosing the right lens for robot arm integration directly affects production efficiency, product quality, and return on investment. This guide will break down everything you need to know about robot arm vision system lenses—from core concepts to practical application, with a focus on Towin’s industry-proven products tailored for global industrial needs.
1. Robot Arm Vision System Overview
A robot arm vision system is an integrated solution that combines optical components, sensors, and software to enable robots to “see” and interact with their environment. Its main components include:
- Optical Lens: The core component that focuses light onto the camera sensor, determining image quality.
- Industrial Camera: Converts optical signals into digital images (e.g., CMOS/CCD sensors).
- Lighting System: Provides stable, uniform illumination to eliminate shadows and enhance contrast.
- Image Processing Algorithm: Analyzes images to extract key information (e.g., object position, size, defects).
- Communication Module: Transmits data between the vision system and the robot arm controller.
This system solves three core challenges for robot arms:
- Precision: Achieves sub-millimeter positioning accuracy for micro-assembly (e.g., electronics manufacturing).
- Flexibility: Adapts to variable object sizes, positions, and orientations (e.g., mixed-model production lines).
- Reliability: Operates 24/7 in harsh industrial environments (e.g., high vibration, temperature fluctuations).
25-Megapixel Robot Vision Lens
2. Core Role of Lenses in Robot Vision
The lens is to a robot’s vision system what the crystalline lens is to the human eye—without it, even the most advanced camera cannot capture usable images. Its key roles include:
- Image Formation: Focuses reflected light from the target onto the camera’s sensor to create a clear, proportional image.
- Distortion Control: Minimizes image warping (barrel/pinchion distortion) to ensure accurate measurement and positioning.
- Field of View (FOV) Adjustment: Determines how much of the environment the robot can “see” (wide FOV for global monitoring, narrow FOV for close-up inspection).
- Light Control: Adjusts light intake via aperture settings to adapt to different lighting conditions (e.g., low-light for machine interiors, high-aperture for outdoor use).
- Depth of Field (DOF) Management: Controls the range of distances where objects remain in focus—critical for uneven surfaces or vibrating conveyor belts.
As noted in industrial vision research, lens distortion of >0.1% can lead to measurement errors of up to 5%—a risk that makes high-precision, low-distortion lenses essential for critical applications like automotive part inspection.
3. Two Lens Mounting Methods for Robot Vision
Robot arm vision systems use two primary lens mounting configurations, each with unique advantages for specific scenarios.
| Category | Eye-in-Hand (EIH) | Eye-to-Hand (ETH) |
| Definition | Lens/camera is mounted directly on the robot arm, moving with it | Lens/camera is fixed in the workspace (e.g., above the production line) |
| Advantages | – Close-range, high-precision imaging | – Wide, stable FOV |
| – Eliminates “blind spots” during arm movement | – No vibration impact | |
| – Adapts to variable workpieces | – Supports multi-robot coordination | |
| Disadvantages | – Limited FOV (tied to arm movement) | – May have blind spots |
| – Susceptible to vibration | – Fixed to specific workspace | |
| – Requires compact lens design | – Less flexible for variable positions | |
| Ideal Use Cases | – Micro-assembly (e.g., PCB component placement) | – Conveyor belt inspection |
| – Precision welding | – Large workpiece measurement | |
| – Object grasping (e.g., robotic pick-and-place) | – Warehouse logistics sorting |
4. Key Parameters of Robot Vision Lenses
Understanding lens parameters is critical for matching the right lens to your robot arm application. Below is a breakdown of core parameters and their impact:
| Parameter | Definition | Impact on Robot Arm Performance | Selection Tips |
| Focal Length | Distance from the lens center to the sensor (mm) | – Short focal length (3.5mm~6mm): Wide FOV for large areas | Choose based on working distance: <0.5m → short focal length; >1m → long focal length |
| – Long focal length (20mm~25mm): Narrow FOV for close-up precision | |||
| Resolution | Maximum image detail the lens can capture (MP) | – Low resolution (8MP): Basic inspection | Match to camera resolution (lens resolution ≥ camera resolution) |
| – High resolution (20MP~25MP): Micro-defect detection | |||
| Distortion | Image warping relative to the real object (%) | – <0.01%: Ultra-low distortion (critical for measurement) | Prioritize <0.1% for industrial measurement; <0.01% for high-precision applications (e.g., semiconductor inspection) |
| – <0.1%: Low distortion (general inspection) | |||
| – >0.1%: High distortion (avoid for precision tasks) | |||
| Mount Type | Physical interface between lens and camera | – C-Mount: Industrial standard (17.526mm flange distance) | C-Mount for large sensors (1.1″~1.2″); M12 for compact robot arms (e.g., collaborative robots) |
| – M12/S-Mount: Compact (M12x0.5 thread) for small cameras | |||
| Field of View (FOV) | Area captured by the lens (degrees) | – Wide FOV (>60°): Global monitoring | Calculate FOV based on workpiece size: FOV ≥ workpiece size + 10% margin |
| – Medium FOV (30°~60°): General inspection | |||
| – Narrow FOV (<30°): Precision targeting | |||
| Aperture (F-Number) | Controls light intake (F2.8~F22) | – Small F-number (F2.8): Low-light performance | F2.8~F4 for low-light environments; F8~F22 for vibrating conveyors |
| – Large F-number (F22): Deep depth of field | |||
| Minimum Object Distance (MOD) | Closest distance the lens can focus on (m) | – 0.1m: Short MOD for close-up tasks | Choose MOD < working distance (e.g., 0.1m MOD for 0.15m working distance) |
| – 0.2m: Longer MOD for large workpieces |
5. Robot Vision Lens Types & Use Cases
Towin offers a range of lens types optimized for robot arm vision, each designed for specific industrial scenarios:
| Lens Type | Key Features | Towin Product Examples | Ideal Use Cases |
| C-Mount Industrial Lenses | – High resolution (20MP~25MP) | C2012028M25, C2511028M20 | – Automotive part measurement |
| – Low distortion (<0.1%) | – PCB defect inspection | ||
| – Manual iris/focus | – Large workpiece positioning | ||
| M12/S-Mount Compact Lenses | – Small size (Φ14x8mm~25.37mm) | CCL132060MPF, S12023004080F | – Collaborative robot arms |
| – Fixed iris | – Miniature assembly (e.g., watch parts) | ||
| – Wide FOV (41°~78°) | – Compact inspection stations | ||
| FA (Factory Automation) Lenses | – Ultra-low distortion (<0.1%) | C2511028M20 | – Industrial measurement systems |
| – High precision | – 3D vision-guided robotics | ||
| – 1.1″ sensor support | – Quality control for small components | ||
| CCTV Security Lenses | – Built-in IR filter | S12023004080F, S03513206628F | – Robot arm surveillance (e.g., theft prevention) |
| – Wide FOV (49°~78°) | – Outdoor robot operations (e.g., agricultural robots) | ||
| – 8MP~13MP resolution | – Low-light inspection (e.g., machine interiors) |
6. Robotic Arm Integrated Vision System Lenses Selection Process
Follow this 6-step workflow to select the perfect lens for your robot arm vision system:
6.1 Define Application Requirements
- What task will the robot perform? (e.g., assembly, inspection, sorting)
- What is the workpiece size and material? (e.g., 50mm metal parts, 10mm plastic components)
- What is the required precision? (e.g., ±0.1mm, ±0.01mm)
- What is the working distance? (e.g., 0.2m, 1m)
6.2 Choose the Mounting Method
- Eye-in-Hand: For close-range, dynamic tasks (e.g., pick-and-place).
- Eye-to-Hand: For fixed-position, wide-area tasks (e.g., conveyor inspection).
6.3 Match Core Parameters
- Focal length: Align with working distance and FOV needs.
- Resolution: Match to camera (e.g., 20MP camera → 20MP+ lens).
- Distortion: <0.1% for measurement; <0.01% for high precision.
- MOD: Ensure it’s less than the working distance.
6.4 Select the Right Mount Type
- C-Mount: For large sensors (1.1″~1.2″) and industrial robots.
- M12/S-Mount: For compact robots and small sensors (1/3.2″~2/3″).
6.5 Test Compatibility
- Check if the lens fits the robot arm’s physical space (e.g., M12 lenses for tight spots).
- Verify image quality under real working conditions (e.g., low light, vibration).
6.6 Finalize and Integrate
- Confirm Towin’s lens meets all requirements (e.g., “Hot Lenses” for high demand).
- Work with Towin’s technical team for integration support (info@towin-elec.com).
7. Towin Robot Arm Vision System Lenses
Towin’s robot arm vision lenses are engineered to address the core demands of industrial automation—precision, stability, and adaptability. Each model is optimized for specific robot arm workflows, with parameters tailored to real-world application scenarios (e.g., high resolution for micro-inspection, low distortion for measurement, compact design for collaborative robots). Below is a detailed breakdown of each lens, including parameter logic and practical application value:
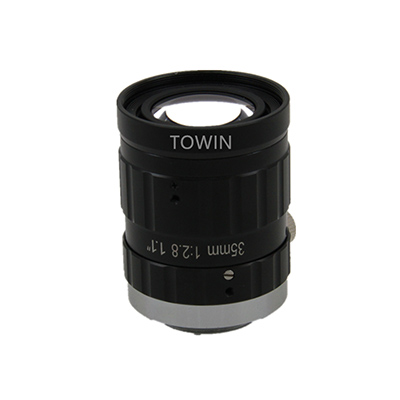
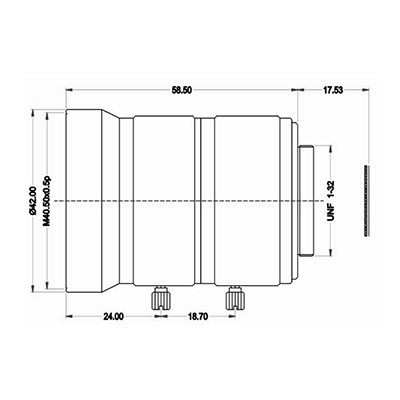
7.1 Towin C2012028M25 (High-Resolution C-Mount Lens)
- Core Parameters & Design Logic:
- Focal length: 20mm (balanced for medium working distances of 0.2m~1.5m, striking a balance between FOV and close-up precision).
- Resolution: 25MP (matches high-end industrial cameras, capturing micro-details like 0.01mm surface defects).
- Distortion: <-0.1% (meets industrial measurement standards, eliminating warping for accurate size calculations).
- Mount type: C-Mount (industrial standard, compatible with 1.2″/1.1″ large sensors for broad FOV coverage).
- Aperture: F2.8~22 (adjustable for low-light environments and deep depth of field, ideal for vibrating conveyor belts).
- MOD: 0.2m (suitable for medium-range inspection tasks without compromising focus clarity).
- Robot Arm Application:
- Automotive component inspection, 3D vision-guided assembly. Delivers sub-millimeter positioning data for large workpieces in dynamic factory environments.
25-Megapixel vision system lenses
7.2 Towin C2511028M20 (C-Mount FA Lens)
- Core Parameters & Design Logic:
- Focal length: 25mm (narrower FOV for close-up precision, perfect for working distances of 0.1m~1m).
- Resolution: 20MP (optimized for industrial measurement, balancing detail and data processing speed).
- Distortion: <0.1% (FA lens-grade precision, suitable for 2D/3D vision-guided robotics).
- Mount type: C-Mount (compatible with mainstream industrial cameras, ensuring easy integration).
- Aperture: F2.8~22 (flexible light control for indoor factory environments with variable lighting).
- MOD: 0.1m (short minimum object distance, enabling close-range inspection of small components like PCB solder joints).
- Robot Arm Application:
- PCB inspection, automotive small parts assembly. Supports ±0.01mm tolerance tasks, balancing speed and accuracy for high-volume production.
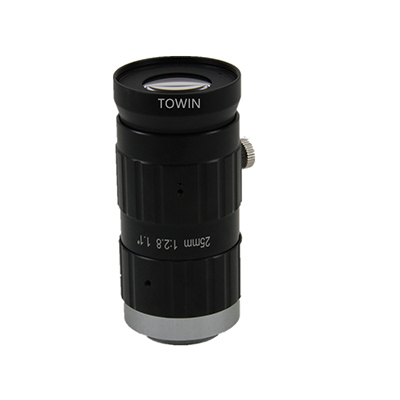

25mm C mount industrial lens
7.3 Towin CCL132060MPF (M12 Compact Wide-Angle Lens)
- Core Parameters & Design Logic:
- Focal length: 6mm (wide-angle, delivering a 52° diagonal FOV for broad coverage in compact spaces).
- Resolution: 8MP (reliable for basic inspection tasks, balancing performance and cost-effectiveness).
- Distortion: <-0.1% (low warping for accurate object positioning, even with a wide FOV).
- Mount type: M12x0.5 (ultra-compact thread mount, ideal for collaborative robots and tight installation spaces).
- Aperture: F3.5 (fixed iris for stable imaging in consistent lighting, reducing setup complexity).
- MOD: 0.1m (short focus distance for close-range sorting and monitoring).
- Robot Arm Application:
- Collaborative robots, logistics sorting. Ultra-compact design fits tight spaces; wide FOV enables multi-object fast picking/sorting.
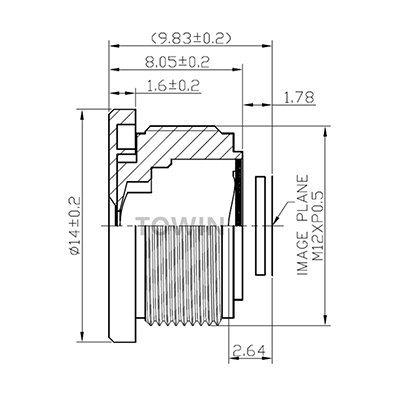
Low distortion wide angle 6mm M12 vision system lenses
7.4 Towin S12023004080F (M12 IR-Cut Outdoor-Ready Lens)
- Core Parameters & Design Logic:
- Focal length: 12mm (medium wide-angle, 49° diagonal FOV for balanced coverage and detail).
- Resolution: 8MP (sufficient for outdoor and low-light inspection tasks).
- Distortion: <-0.1% (maintains image integrity for outdoor robot operations like agricultural sorting).
- Mount type: M12x0.5 (compact, compatible with small-format cameras for mobile robots).
- Aperture: F8.0 (fixed iris with deep depth of field, reducing motion blur in dynamic outdoor environments).
- MOD: 0.1m (versatile for both close-up inspection and medium-range monitoring).
- Key Add-On: Built-in IR filter (blocks infrared light for accurate color reproduction in sunlight, while enhancing low-light visibility).
- Robot Arm Application:
- Outdoor logistics/agricultural robots, low-light inspection. Resists lighting changes, reduces motion blur for dynamic scene recognition.
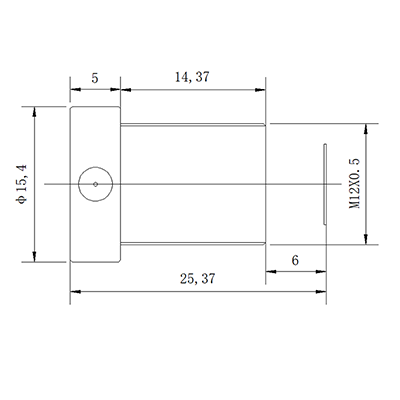
vision system lenses
7.5 Towin S03513206628F (M12 Ultra-Low Distortion Lens)
- Core Parameters & Design Logic:
- Focal length: 3.5mm (ultra-wide-angle, 78° diagonal FOV for maximum coverage).
- Resolution: 13MP (high detail for micro-assembly, bridging the gap between basic and premium lenses).
- Distortion: <0.01% (ultra-low warping—critical for high-precision micro-measurement and semiconductor inspection).
- Mount type: M12x0.5 (compact, suitable for small robots and high-density production lines).
- Aperture: F2.8 (large aperture for low-light performance, ideal for indoor micro-assembly stations).
- MOD: 0.1m (short focus distance for close-up work on tiny components like microchips).
- Robot Arm Application:
- Semiconductor micro-assembly. Ultra-wide FOV + sub-millimeter precision for micro-component positioning/detection.
Ultra-Low-distortion 13-Megapixel M12 CCTV lens
7.6 Towin Robotic arm integrated vision system lenses: Complete Specification Table
| Model | Mount Type | Focal Length | Resolution | Distortion | FOV (Diagonal) | Aperture | MOD | Key Advantages | Ideal Robot Arm Tasks |
| C2012028M25 | C-Mount | 20mm | 25MP | <-0.1% | 51.5° (1.2″) / 47.5° (1.1″) | F2.8~22 | 0.2m | 25MP high res; 1.2″ sensor support; manual iris | High-precision measurement; large workpiece inspection; 3D vision guiding |
| C2511028M20 | C-Mount | 25mm | 20MP | <0.1% | 38° (1.1″) | F2.8~22 | 0.1m | FA lens precision; short MOD; low distortion | PCB component inspection; automotive small parts assembly; surface defect detection |
| CCL132060MPF | M12x0.5 | 6mm | 8MP | <-0.1% | 52° | F3.5 | 0.1m | Ultra-compact (Φ14x8mm); wide angle; fixed iris | Collaborative robot arms; compact inspection stations; logistics sorting (small parcels) |
| S12023004080F | M12x0.5 | 12mm | 8MP | <-0.1% | 49° | F8.0 | 0.1m | Built-in IR filter; durable; deep DOF | Outdoor robot operations; low-light inspection; workspace security monitoring |
| S03513206628F | M12x0.5 | 3.5mm | 13MP | <0.01% | 78° | F2.8 | 0.1m | Ultra-low distortion; ultra-wide FOV; high res | High-precision micro-assembly; wide-area surveillance; semiconductor inspection |
8. Scenario-Specific Lens Recommendation
Below are tailored lens solutions for common robot arm applications, based on industry best practices:
8.1 Electronics Manufacturing (e.g., PCB Assembly)
- Requirements: High resolution, low distortion, short working distance.
- Recommended Lens: Towin C2511028M20 (20MP, <0.1% distortion, 0.1m MOD).
- Why: Captures micro-defects (e.g., solder cracks) and ensures precise component placement.
8.2 Automotive Parts Inspection (e.g., Engine Components)
- Requirements: Large sensor support, high resolution, deep DOF.
- Recommended Lens: Towin C2012028M25 (25MP, 1.2″ sensor, F2.8~22).
- Why: Covers large workpieces and maintains focus on uneven metal surfaces.
8.3 Logistics Sorting (e.g., Parcel Handling)
- Requirements: Wide FOV, compact design, stable imaging.
- Recommended Lens: Towin CCL132060MPF (6mm, 52° FOV, Φ14x8mm).
- Why: Fits collaborative robots and captures multiple parcels at once.
8.4 Outdoor Robot Operations (e.g., Agricultural Robots)
- Requirements: IR filter, weather resistance, low-light performance.
- Recommended Lens: Towin S12023004080F (built-in IR filter, F8.0).
- Why: Adapts to sunlight and low-light conditions, ensuring consistent imaging.
8.5 High-Precision Micro-Assembly (e.g., Semiconductors)
- Requirements: Ultra-low distortion, high resolution, short MOD.
- Recommended Lens: Towin S03513206628F (<0.01% distortion, 13MP, 0.1m MOD).
- Why: Eliminates measurement errors and captures tiny components (e.g., microchips).
Ultra-Low-distortion 13-Megapixel M12 CCTV lens
FAQs
Q1: How do I choose between Eye-in-Hand and Eye-to-Hand mounting?
A: Choose Eye-in-Hand if your robot needs to work with variable workpiece positions (e.g., pick-and-place). Choose Eye-to-Hand for fixed workflows (e.g., conveyor inspection) to avoid vibration impacts.
Q2: What happens if the lens resolution is lower than the camera resolution?
A: The camera’s full potential will be wasted—images will be limited by the lens’s resolution, leading to blurry details and missed defects. Always ensure lens resolution ≥ camera resolution.
Q3: Do Towin lenses support customization for unique robot arm designs?
A: Yes! Towin offers custom lens design and manufacturing (info@towin-elec.com) to fit specific sizes, focal lengths, or environmental requirements (e.g., high-temperature resistance).
Q4: How do I maintain robot arm vision lenses in harsh industrial environments?
A: – Clean lenses with a microfiber cloth (avoid alcohol).
- Use lens caps when not in use.
- Check for vibration damage quarterly (Towin lenses have durable structures for harsh conditions).
Q5: Can Towin lenses work with third-party cameras (e.g., Axis, Toshiba Teli)?
A: Yes! All Towin lenses comply with industry standards (C-Mount, M12x0.5) and are compatible with most industrial cameras. Contact our team for specific compatibility checks.
Conclusion
Robot arm vision system lenses are the “unsung heroes” of industrial automation—they directly determine whether a robot can “see” clearly, act precisely, and adapt to dynamic workflows. Towin’s range of C-Mount and M12 lenses, with their low distortion (<0.01%~<-0.1%), high resolution (8MP~25MP), and compact designs, are engineered to meet the diverse needs of global manufacturers.
Whether you’re building a collaborative robot for electronics assembly or an outdoor robot for agriculture, Towin has a lens solution tailored to your needs. For personalized recommendations or technical support, contact us today at info@towin-elec.com—our team of optical experts is ready to help you optimize your robot arm vision system.