Fixed Focal Lens vs Varifocal Lens: Which offers better MTF for security?
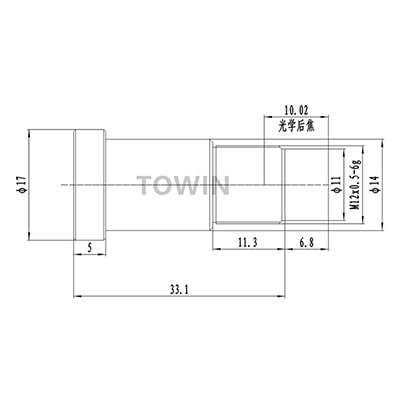
M12 8mm CCTV lens with IR corrected
01/26/20261/3″ 2.3mm 4-Megapixel Wide angle lens
01/27/2026Table of Contents
- Introduction
- MTF in Security Surveillance
- Fixed Focal Lens: Superior MTF for Critical Security Points
- Varifocal Lens: Flexibility vs. MTF Tradeoffs
- High-End Varifocal Lenses: Narrowing the MTF Gap
- Fixed Focal Lens vs Varifocal Lens: MTF Performance Comparison
- Choosing the Right Lens for Security: MTF-Driven Strategy
- Security Application Scenario Recommendations
- FAQs
- Conclusion
Key Takeaways
- MTF Core Value: The MTF is key to a security lens, determining sharpness, contrast, and detail reproduction in footage.
- Fixed Focal Lens MTF Advantages: Simple structure, more stable MTF performance and higher peak values at a fixed focal length, suitable for security scenarios with extremely high detail accuracy requirements.
- Varifocal Lens Trade-offs: Offers the advantage of flexible angle of view adjustment, but complex optical structure; MTF performance fluctuates with focal length, requiring a trade-off between flexibility and image quality.
- High-end Zoom Breakthrough: Through special optical design and materials, high-end Varifocal lenses can significantly narrow the MTF gap with fixed-focus lenses, balancing flexibility and image quality.
- Core Selection Logic: Guided by the angle of view requirements and detail priorities of the surveillance scenario, and considering the budget, choose either a fixed-focus or high-end Varifocal lens.
Introduction
In security surveillance systems, image quality is the cornerstone of effective threat detection, evidence collection, and situational awareness. Among the numerous factors affecting image quality, the Modulation Transfer Function (MTF) of the lens plays a decisive role—it quantifies how well a lens reproduces fine details and contrast from the subject to the image sensor. For foreign trade buyers and security system integrators, choosing between Fixed Focal lenses and Varifocal lenses often boils down to a trade-off between MTF performance and application flexibility. This article analyzes MTF traits of two lens types and offers security-scenario recommendations for informed purchases.
MTF in Security Surveillance
MTF is a quantitative tool to evaluate the optical performance of lenses, which reflects the ability of a lens to transfer the contrast of the original scene to the image. It is expressed by a curve with a value ranging from 0 to 1:
- A value closer to 1 indicates the lens can reproduce details and contrast more accurately, with sharper images.
- A value closer to 0 means severe loss of details and contrast, resulting in blurred or foggy images.
In security applications, MTF is critical for the following scenarios:
- License plate recognition: Requires high MTF to clearly capture small characters on license plates.
- Face recognition: Depends on accurate detail reproduction of facial features, which is directly related to MTF performance.
- Low-light surveillance: High MTF lenses can retain more details in low-light environments, improving detection accuracy.
- Long-distance monitoring: For scenarios such as perimeter security, high MTF ensures clear imaging of distant targets.

2/3″ 6-15mm Auto Iris F1.4 C mount IR corrected Zoom CCTV lens
Fixed Focal Lens: Superior MTF for Critical Security Points
Fixed Focal lens have a fixed focal length, allowing optical engineers to optimize every aspect of their design for a single focal point. This specialization is why Fixed Focal lenses consistently outperform Varifocal lenses in MTF—especially in the harsh conditions of security surveillance.
A. Why Fixed Focal Lenses Excel in MTF
- Simplified Optical Design: Fixed Focal lenses typically use 3–8 lens elements (vs. 10+ for Varifocal lenses) and lack the complex moving groups needed for zoom functionality. This simplicity lets engineers correct aberrations (spherical, chromatic, coma) with precision across the entire field of view and aperture range. The result is flat MTF curves, with minimal detail loss at the edges.
- Mechanical Stability: No moving parts mean no mechanical play, wear, or optical misalignment over time. For 24/7 security deployments—especially on vibrating poles, highway overpasses, or windy rooftops—Fixed Focal lenses maintain consistent MTF for years, while Varifocal lenses may suffer from degraded performance as gears wear or lenses shift.
- Superior Light Transmission: Fewer lens elements reduce light reflection and absorption, boosting light transmission (T-stop). Large-aperture primes (f/1.4, f/1.8) are also easier to design, delivering more light to the sensor in low-light conditions. This keeps MTF stable at night, avoiding the detail loss caused by underexposure.
B. Ideal Security Applications for Fixed Focal Lenses
Fixed Focal lenses are the go-to choice for high-priority surveillance points where MTF and reliability are non-negotiable:
- License Plate Recognition (LPR): Highway tolls, parking garage entrances, and traffic intersections require sharp detail at specific distances. Fixed Focal lenses (e.g., 25mm, 35mm) optimized for LPR deliver consistent MTF at the spatial frequencies needed to read plates—even at night or in backlight.
- Facial Recognition: Building lobbies, access control points, and retail checkout areas need clear facial features. Wide-aperture primes ensure low-light MTF stability, while edge-to-center sharpness captures full facial details without blurring.
- Low-Light Environments: Unlit alleys, rural perimeters, and nighttime industrial sites benefit from Fixed Focal lenses’ superior light transmission. IR-corrected primes maintain MTF when paired with IR illuminators, avoiding the “ghosting” or blur of uncorrected lenses.
- Long-Distance Fixed Points: High-magnification Fixed Focal lenses (e.g., 85mm, 100mm) offer better MTF at long ranges than Varifocal lenses, making them ideal for monitoring fences, power plants, or waterfronts.
Varifocal Lens: Flexibility vs. MTF Tradeoffs
Varifocal lens offer variable focal lengths (e.g., 10–22mm, 20–70mm), enabling operators to switch between wide-angle coverage and telephoto detail without changing lenses. This flexibility is valuable, but it comes with inherent MTF compromises—engineers must balance performance across the entire zoom range, not just one focal point.
A. Inherent MTF Limitations of Varifocal Lenses
- Compromised Design Across Focal Lengths: A Varifocal lens cannot be optimized for every focal point. Typically, MTF is strongest at mid-range focal lengths, with significant drop-off at extreme wide or telephoto ends. For example, a 12–36mm zoom may perform well at 24mm but lack edge sharpness at 12mm and suffer from softness at 36mm—critical flaws for security’s need for consistent detail.
- Mechanical Complexity: Moving lens groups introduce alignment errors, especially over time. Temperature fluctuations (hot days, cold nights) can expand or contract lens barrels, shifting optics and degrading MTF. In high-vibration environments, Varifocal lenses are more prone to MTF instability than primes.
- Reduced Light Efficiency: More lens elements and coatings increase light loss. Varifocal lenses also rarely offer large apertures at telephoto lengths (e.g., a 24–70mm zoom may drop from f/2.8 to f/4 at 70mm), reducing low-light performance and MTF in nighttime scenarios.
B. Suitable Security Applications for Varifocal Lenses
Despite MTF limitations, Varifocal lenses fill a vital niche in security systems where flexibility outweighs absolute sharpness:
- Wide-Area Coverage: City squares, stadiums, and large campuses need both panoramic views and the ability to zoom in on suspicious activity. PTZ (Pan-Tilt-Zoom) cameras—standard in these settings—rely on Varifocal lenses to deliver flexible monitoring.
- Temporary Deployments: Construction sites, event venues, or temporary checkpoints benefit from Varifocal lenses’ adaptability. Operators can adjust focal length without repositioning cameras, reducing installation time and cost.
- Multi-Purpose Monitoring: Small retail stores or office lobbies may use a single zoom camera to cover both the entrance (wide-angle) and cash register (telephoto). While MTF is not perfect, it suffices for non-critical identification.

C-mount IR corrected CCTV Vari-Focal lens
High-End Varifocal Lens: Narrowing the MTF Gap
With the advancement of optical technology, high-end Varifocal lens adopt advanced designs and materials to significantly narrow the MTF gap with Fixed Focal lenses. Key technologies include:
- Special optical materials: Using low-dispersion glass (ED glass) and aspherical lenses to reduce aberrations and improve MTF stability across focal lengths.
- Precision optical design: Optimizing lens group layout and zoom mechanism to minimize MTF loss during zooming, ensuring consistent performance at all focal lengths.
- Image stabilization technology: Equipping optical image stabilization (OIS) to compensate for shaking caused by zooming or external factors, maintaining MTF stability.
- Multi-layer coating: Adopting anti-reflection coating to improve light transmittance and contrast, enhancing MTF in complex light environments.
Fixed Focal Lens vs Varifocal Lens: MTF Performance Comparison
| Performance Indicator | Fixed Focal Lens | Ordinary Varifocal Lens | High-End Varifocal Lens |
| Peak MTF Value | High (close to 1 at fixed focal length) | Medium (fluctuates across focal lengths) | High (stable across most focal lengths) |
| Edge MTF Performance | Excellent (little loss) | Average (obvious loss at extreme focal lengths) | Good (slight loss at extreme ends) |
| MTF Stability | Very stable (fixed focal length, no fluctuation) | Unstable (varies with focal length) | Stable (minor fluctuation) |
| Optical Aberration | Low | Medium-High | Low |
| Flexibility | Low (fixed focal length) | High | High |
| Cost-Effectiveness | High (excellent MTF at a reasonable price) | Medium (balance between cost and performance) | Low (high cost for advanced technology) |
Choosing the Right Lens for Security: MTF-Driven Strategy
The optimal security lens strategy prioritizes MTF where it matters most, using Varifocal lenses only for flexible coverage. Follow these guidelines to balance performance and practicality:
- Adopt a “Prime-First” Approach: Use primes for all critical capture points (LPR, facial recognition, low-light areas). This ensures maximum MTF and reliability, the foundation of actionable security footage.
- Evaluate MTF Curves Critically: When comparing lenses, focus on high spatial frequencies (200lp/mm+) and edge-to-center consistency. Avoid lenses with steep MTF drop-off at the edges—common in budget zooms.
- Match Lens to Sensor Resolution: 4K/8K cameras require lenses with strong high-frequency MTF. A 4K camera paired with a low-MTF zoom will produce soft footage; opt for 4K-optimized primes or premium zooms.
- Consider Environmental Factors: For outdoor, high-vibration, or extreme-temperature sites, primes are more reliable. Use high-end zooms only if flexibility is non-negotiable, and prioritize weather-sealed models.
Security Application Scenario Recommendations
1. Fixed Focal Lens Application Scenarios
- Access control points: Fixed monitoring of access gates, requiring clear face and ID card recognition, with Fixed Focal lenses ensuring high MTF for detail capture.
- ATM machines: Monitor the area around the machine, needing to clearly record user faces and operation details, with Fixed Focal lenses providing stable sharpness.
- Key facility perimeters: Fixed monitoring of fences, doors, and windows of power stations, data centers, etc., with Fixed Focal lenses ensuring clear imaging of abnormal targets.
- Low-light environments: Warehouses, outdoor night monitoring, where Fixed Focal lenses’ high light transmittance and MTF performance ensure clear imaging in low light.
2. Varifocal Lens Application Scenarios
- Large public areas: Shopping malls, airports, stations, where one lens can cover both wide-area monitoring and close-up detail inspection (such as crowd anomalies).
- Outdoor large-scale venues: Stadiums, industrial parks, requiring remote zoom to monitor distant targets without on-site lens replacement.
- Mobile monitoring systems: Vehicle-mounted surveillance, drone monitoring, where Varifocal lenses adapt to dynamic scene changes and adjust perspectives in real time.
- Multi-functional monitoring points: Scenarios needing both wide-angle patrol and close-up verification, such as community entrances and exits.

IR-corrected CS-mount Fixed Focal lens
FAQs
Q: What MTF value is suitable for security surveillance?
A: For general security monitoring, a lens with a central MTF value ≥0.7 (at 50 lp/mm) is recommended; for license plate/face recognition, the central MTF should be ≥0.8 to ensure clear detail reproduction.
Q: Can a high-end Varifocal lens completely replace a Fixed Focal lens in terms of MTF?
A: Currently, high-end Varifocal lenses can achieve MTF performance close to Fixed Focal lenses at middle focal lengths, but at extreme focal lengths (ultra-wide or ultra-telephoto), Fixed Focal lenses still have a slight advantage. The choice depends on whether the scenario requires extreme focal length use.
Q: Does the sensor resolution affect the performance of the lens MTF?
A: Yes. A high-resolution sensor (such as 4K, 8K) requires a lens with matching MTF performance. If the lens MTF is low, the sensor’s high resolution cannot be fully utilized, resulting in wasted performance.
Q: How to test the MTF of a lens in practical applications?
A: You can use standard MTF test charts, capture images under standard light conditions, and observe the clarity of the chart’s line pairs and contrast to evaluate MTF performance; professional users can use optical testing instruments for quantitative measurement.
Q: Is there a cost-effective solution for balancing MTF and flexibility?
A: Yes. For most scenarios, using Fixed Focal lenses for key detail points and ordinary Varifocal lenses for wide-area dynamic monitoring can balance MTF performance, flexibility, and budget.
Conclusion
In security applications, Fixed Focal lens excel in MTF performance, making them the first choice for scenarios requiring high-precision detail capture; Varifocal lenses win with flexibility, adapting to dynamic multi-scene monitoring needs. High-end Varifocal lenses, relying on advanced optical technology, have narrowed the MTF gap with Fixed Focal lenses, providing a high-quality alternative for scenarios requiring both flexibility and image quality.
When selecting lenses for foreign trade security projects, it is necessary to comprehensively consider factors such as scene requirements, detail priority, budget, and sensor resolution. By taking MTF performance as the core evaluation index and combining application flexibility, you can choose the most suitable lens solution, ensuring the effectiveness and reliability of the security system.