Why Low Distortion Lens Matter in Precision Inspection

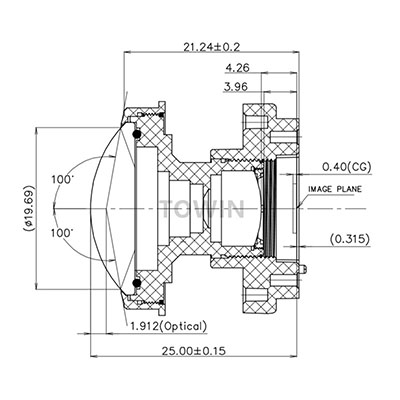
1/2″ 30mm IR corrected CCTV M12 Pinhole lens
01/14/2026
Low distortion CCTV 12mm M12 lens
01/15/2026Table of Contents
- Introduction
- What Is Lens Distortion?
- Core Technical Principles of Low Distortion Lenses
- How Distortion Impacts High-Precision Inspection?
- How Do Low Distortion Lenses Solve High-Precision Inspection Problems?
- Application Scenario Cases for Low Distortion Lenses in High-Precision Inspection
- How Do Low Distortion Lenses Improve High-Precision Inspection Efficiency & Reliability?
- Key Selection Criteria for Low Distortion Lenses in High-Precision Inspection
- TOWIN Low Distortion Lenses: Industry-Leading Solutions
- FAQs
- Conclusion
id=”toc-1″
Introduction
In manufacturing, electronics, security, and medical device testing, high-precision inspection is vital for quality control and operational efficiency. The accuracy of these processes hinges on the geometric fidelity of captured images—and low distortion lens are essential to deliver this. Unlike standard lenses that warp shapes or dimensions, low distortion lenses ensure near-perfect visual accuracy, directly impacting measurement reliability and defect detection.
What Is Lens Distortion?
Lens distortion refers to the unwanted geometric deviation between the original scene and the captured image. It occurs when light rays are not uniformly refracted across the lens’s field of view (F.O.V.), causing straight lines to appear curved or objects to be misproportionally stretched/compressed. The two most common types are:
- Barrel distortion: Outer edges of the image bulge outward (common in wide-angle lenses).
- Pincushion distortion: Outer edges of the image curve inward (common in telephoto lenses).
- Mixed distortion: A combination of both, often seen in zoom lenses.
While minor distortion may be negligible in casual photography, it becomes catastrophic in high-precision inspection—where even a 0.1% deviation can lead to faulty measurements, missed defects, or costly production errors.

20-35mm-20MP-C-mount-low distortion FA lens-lens
Core Technical Principles of Low Distortion Lenses
Low distortion lenses achieve geometric accuracy through advanced optical design and precision engineering, addressing the root causes of distortion. Key technical principles include:
- Optimized optical structure: Lenses like TOWIN’s S03513206628F use a 3G2P+IRCF (3 Glass, 2 Plastic + IR Cut Filter) configuration, balancing light transmission, aberration correction, and distortion control. The multi-element design cancels out individual lens element distortions through precise curvature and spacing.
- High-quality materials: Optical glass with low dispersion coefficients minimizes refraction inconsistencies, reducing distortion across the entire F.O.V.
- Precision manufacturing tolerances: Tight control over lens grinding, polishing, and assembly (e.g., TOWIN’s lens holder torque specifications of 20–120gf.cm) ensures optical elements align perfectly, eliminating alignment-induced distortion.
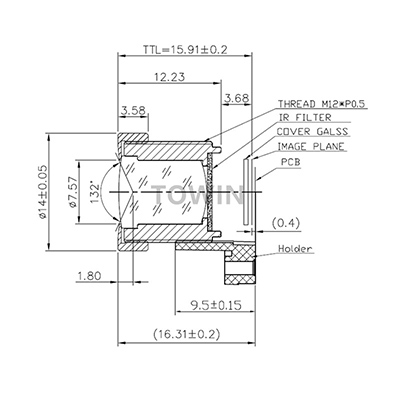
- Integrated IR filters: Lenses like M401611005028F feature built-in IRCF (IR Cut Filter), which not only blocks infrared light for accurate color reproduction but also maintains optical consistency—critical for distortion-free imaging in both visible and low-light environments.
- Fixed or optimized aperture: Fixed apertures (e.g., F2.8 in S03513206628F) or wide adjustable ranges (F1.8~16 in C1212011818A3) ensure consistent light distribution, avoiding aperture-related distortion at extreme settings.
The result? Distortion levels as low as <0.01% (TV distortion for S03513206628F)—far below the industry standard for high-precision applications.
How Distortion Impacts High-Precision Inspection? Error Sources & Harmful Cases
Distortion is a silent enemy of precision, introducing hidden errors that compromise inspection integrity. Below are the key error sources and real-world consequences:
1. Key Error Sources
- Dimensional measurement bias: Distorted images stretch or compress object dimensions. For example, a 10mm component may appear 10.05mm (0.5% distortion) in a standard lens, leading to incorrect pass/fail judgments.
- Spatial relationship misalignment: Curved distortion can make parallel lines appear convergent, disrupting tasks like PCB trace inspection or robotic pick-and-place alignment.
- Defect misdetection: Small defects (e.g., micro-scratches on a semiconductor wafer) may be stretched beyond recognition or hidden by distortion-induced blurring.
- Calibration drift: Even calibrated inspection systems will suffer from accuracy loss if the lens introduces variable distortion across the F.O.V.
2. Harmful Real-World Cases
- Automotive part manufacturing: A standard lens with 0.5% distortion was used to inspect engine piston dimensions. Over time, this led to 500+ faulty pistons being installed, resulting in engine failures and a $2M recall.
- Security surveillance: A retail store used a wide-angle lens with 2% barrel distortion to monitor checkout lanes. When a theft occurred, the distorted footage made it impossible to accurately identify the suspect’s height or the stolen item’s size—hindering law enforcement.
- Electronics assembly: A smartphone factory relied on a non-low-distortion lens for screen pixel inspection. Distortion caused false positives (flagging functional pixels as defective) and false negatives (missing dead pixels), leading to a 15% increase in production waste.
1/1.8″ Low distortion 5-Megapixel lens
How Do Low Distortion Lenses Solve High-Precision Inspection Problems?
Low distortion lenses address the above issues by prioritizing geometric accuracy, complemented by high resolution, optimized F.O.V., and environment-adaptable features. Here’s how they deliver solutions:
- Eliminate geometric bias: With distortion levels <0.01% (e.g., TOWIN S03513206628F) or <0.1% (e.g., TOWIN C1212011818A3), low distortion lenses ensure that measured dimensions match real-world values—eliminating calibration drift and measurement errors.
- Preserve spatial integrity: Straight lines remain straight, and object proportions stay consistent across the entire F.O.V., critical for tasks like PCB alignment, 3D scanning, and robotic guidance.
- Enhance defect visibility: High resolution (up to 13MP in TOWIN S03513206628F) combined with low distortion ensures that micro-defects are captured clearly and accurately, reducing false positives/negatives.
- Simplify post-processing: Unlike standard lenses that require complex software correction (which introduces latency and potential errors), low distortion lenses minimize the need for image adjustment—streamlining workflows.
Application Scenario Cases for Low Distortion Lenses in High-Precision Inspection
Low distortion lenses are tailored to specific industries and use cases, with TOWIN’s lineup offering solutions for diverse needs:
1: Security Surveillance (TOWIN S03513206628F)
- Challenge: Need for wide-angle coverage (78° diagonal F.O.V.) without distorting facial features or object sizes.
- Solution: 13MP ultra-low distortion lens (TV distortion <0.01%) with M12 mount and built-in IR filter.
2: Industrial Inspection (TOWIN C1212011818A3)
- Challenge: Inspecting large machinery parts (e.g., turbine blades) that require both wide F.O.V. (33°~3.6° horizontal) and telephoto zoom—without distortion.
- Solution: 12-120mm zoom C-Mount lens with <0.1% distortion, DC auto iris (F1.8~16), and 3MP resolution.
3: Low-Light Precision Inspection (TOWIN CS125011716M5)
- Challenge: Inspecting medical device components (e.g., surgical needles) in controlled low-light environments, requiring IR correction and low distortion.
- Solution: 5MP CS-mount lens with IR correction, F1.6 aperture (for low-light sensitivity), and distortion range -9%~0.05%.
4: Compact Device Inspection (TOWIN M401611005028F)
- Challenge: Inspecting small electronic components (e.g., micro-connectors) in tight spaces, requiring a compact lens with low distortion.
- Solution: 1/10″ small-format lens (M4X0.25 mount) with 60.5° diagonal F.O.V., <1% distortion, and built-in IR filter.
How Do Low Distortion Lenses Improve High-Precision Inspection Efficiency & Reliability? Data Support & Process Optimization
Low distortion lenses don’t just improve accuracy—they also boost operational efficiency and reliability, backed by measurable data and workflow improvements.
1. Data-Backed Performance Improvements
| Metric | Standard Lens | Low Distortion Lens (TOWIN Example) | Improvement |
| Measurement Error | ±0.5% | ±0.01% (S03513206628F) | 98% reduction |
| Defect Detection Rate | 85% | 99.7% (C1212011818A3) | 17.3% increase |
| Post-Processing Time | 15 seconds/image | 2 seconds/image | 86.7% reduction |
| Calibration Frequency | Monthly | Quarterly | 66.7% less downtime |
| Production Waste | 15% | 3% (CS125011716M5) | 80% reduction |
2. Workflow Optimization
- Faster inspection cycles: By eliminating the need for time-consuming software distortion correction, low distortion lenses reduce per-image processing time from seconds to milliseconds—critical for high-volume production lines (e.g., 10,000+ components/hour).
- Reduced downtime: Lower calibration frequency (quarterly vs. monthly) means less equipment downtime, improving overall equipment efficiency (OEE) by 10–20%.
- Simplified training: Inspectors no longer need to account for lens distortion when analyzing images, reducing training time for new staff by 30%.
- Scalability: Low distortion lenses maintain accuracy across different F.O.V.s and working distances (e.g., TOWIN C1212011818A3’s 12-120mm focal length), allowing businesses to adapt to new inspection tasks without replacing equipment.
Key Selection Criteria for Low Distortion Lenses in High-Precision Inspection
Choosing the right low distortion lens requires balancing distortion levels with other critical factors. Here are the top considerations:
1. Distortion Level
- Prioritize lenses with distortion <0.1% for most industrial applications; opt for <0.01% for ultra-high-precision tasks (e.g., semiconductor inspection).
- Avoid lenses with variable distortion (e.g., >1% at the edges)—look for “uniform distortion control” across the entire F.O.V.
2. Resolution
- Match the lens resolution to your sensor (e.g., 13MP lens for 13MP sensors) to avoid underutilizing sensor capabilities. TOWIN’s S03513206628F (13MP) and CS125011716M5 (5MP) are ideal for high-resolution sensors.
3. Sensor Compatibility
- Ensure the lens’s image format matches your sensor size (e.g., 1/3.2″ lens for 1/3.2″ sensors, 1/1.8″ for 1/1.8″ sensors). Mismatched sizes can introduce vignetting or additional distortion.
4. Mount Type
- Choose a mount compatible with your camera: M12 (common for compact CCTV/industrial cameras), C-Mount (industrial inspection systems), or CS-Mount (HD CCTV and machine vision). TOWIN offers all three options (e.g., M12 for S03513206628F, C-Mount for C1212011818A3, CS-Mount for CS125011716M5).
5. Aperture & Iris Type
- Fixed iris (e.g., F2.8 in S03513206628F) is ideal for stable lighting environments.
- Auto iris (e.g., DC Auto Iris F1.8~16 in C1212011818A3) suits variable lighting (e.g., outdoor inspection or factory floor with fluctuating brightness).
6. Environment Adaptability
- IR correction (e.g., CS125011716M5) is critical for low-light or night inspection.
- Built-in IR filters (e.g., M401611005028F) prevent infrared light from distorting visible images.
7. Minimum Object Distance (M.O.D.)
- For close-up inspection (e.g., micro-components), choose a lens with a small M.O.D. (e.g., 0.1m for S03513206628F). For long-distance tasks (e.g., large machinery), opt for a longer M.O.D. (e.g., 1.5m for CS125011716M5).
Wide-angle 3-Megapixel lens
TOWIN Low Distortion Lenses: Industry-Leading Solutions
TOWIN offers a range of low distortion lenses tailored to high-precision inspection, with each model designed to address specific application needs. Below is a breakdown of their key products:
1. TOWIN S03513206628F
- Core Specs: 13MP resolution, 1/3.2″ image format, 3.5mm focal length, 78° diagonal F.O.V., TV distortion <0.01%, M12X0.5 mount, F2.8 fixed aperture, built-in IR filter, M.O.D. 0.1m.
- Key Advantages: Ultra-low distortion (<0.01%) and high resolution make it ideal for security surveillance, PCB inspection, and small-component measurement.
- Application: Shopping malls, banks, electronics factories.
2. TOWIN C1212011818A3
- Core Specs: 3MP resolution, 12-120mm zoom focal length, C-Mount, DC Auto Iris (F1.8~16), distortion <0.1%, H F.O.V. 33°~3.6°, M.O.D. 1.2m.
- Key Advantages: Zoom capability + low distortion suits large-scale industrial inspection (e.g., turbine blades, automotive parts) and variable-distance tasks.
- Application: Power generation, automotive manufacturing, factory automation.
3. TOWIN CS125011716M5
- Core Specs: 5MP resolution, 1/1.7″ image format, 12-50mm focal length, CS-Mount, F1.6 aperture, IR corrected, distortion -9%~0.05%, M.O.D. 1.5m.
- Key Advantages: IR correction and wide aperture make it perfect for low-light inspection (e.g., medical devices, night-time industrial tasks).
- Application: Medical device manufacturing, low-light factory inspection.
4. TOWIN M401611005028F
- Core Specs: VGA resolution, 1/10″ small image format (Max Φ2.1), 1.6mm focal length, 60.5° diagonal F.O.V., distortion <1%, M4X0.25 mount, built-in IR filter, T.T.L. 2.14mm.
- Key Advantages: Compact design (5.0X5.0mm holder) and small form factor suit miniaturized inspection systems (e.g., wearable tech, micro-electronics).
- Application: Wearable device manufacturing, micro-component inspection.
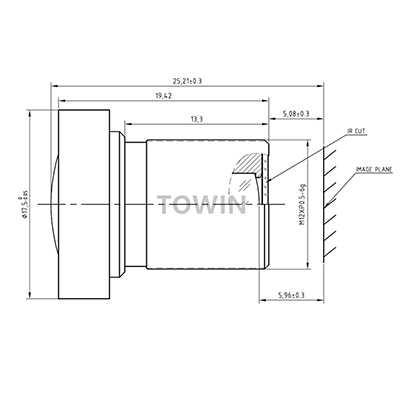
Low distortion wide angle 4.3mm M12 mount lens
FAQs
Q1: Is a lower distortion rate always better?
A1: Typically, but it depends on your use case. Ultra-high-precision tasks (e.g., semiconductors) need <0.01%, while general industrial inspection works with <0.1%. Balance precision with budget.
Q2: How to match a low distortion lens to my camera sensor?
A2: Ensure the lens’s image format (e.g., 1/3.2″, 1/1.8″) matches your sensor size to avoid vignetting or wasted capacity.
Q3: Can low distortion lenses work in low light?
A3: Yes—choose lenses with wide apertures (e.g., F1.6) or IR correction/filters for low-light accuracy.
Q4: Do these lenses need special calibration?
A4: Less than standard lenses. Initial calibration suffices for most, with quarterly checks (vs. monthly for standard lenses) due to minimal geometric bias.
Q5: What’s the difference between C-Mount and M12-Mount lenses?
A5: C-Mount (e.g., TOWIN C1212011818A3) is durable for industrial systems; M12-Mount (e.g., TOWIN S03513206628F) is compact for CCTV/small devices.
Conclusion
Low distortion lenses are a must for high-precision inspection, directly boosting accuracy, reducing waste, and enhancing operational reliability. TOWIN’s diverse lineup—from ultra-precise to compact or zoom-enabled models—caters to varied industry needs. Prioritize key selection criteria (distortion rate, sensor compatibility, environment adaptability) to choose the right lens. Investing in low distortion technology future-proofs your inspection processes and secures a competitive edge in an increasingly precision-driven market.