Fisheye Lens: How It Works

Multi-pinhole array lens
10/15/2025
Low-reflection low-distortion lens
10/15/2025Photography enthusiasts and professionals alike are drawn to the Fisheye Lens for its ability to transform ordinary scenes into dramatic, immersive masterpieces. But how does this unique lens achieve its signature curved, ultra-wide effect? Whether you’re a beginner or a seasoned pro, understanding Fisheye Lens: How It Works is essential to unlocking its full potential.
What Is a Fisheye Lens?
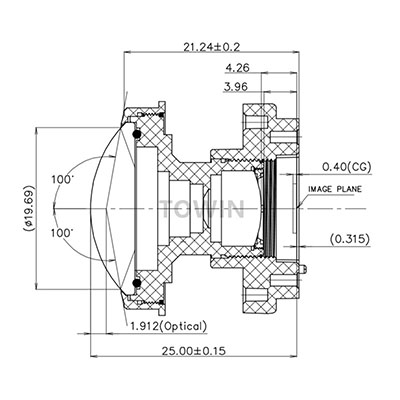
A Fisheye Lens is an ultra-wide-angle optical device designed to capture a hemispherical view of the world—typically 180° or more. Unlike standard wide-angle lenses, which distort edges minimally, Fisheye Lenses embrace distortion to create a spherical, convex effect. This results in images where straight lines curve dramatically, and the entire frame feels like a window into another dimension.
There are two primary types of Fisheye Lenses:
- Circular Fisheye: Projects a circular image within the frame, leaving black corners.
- Full-Frame Fisheye: Fills the entire rectangular frame with a distorted but wider perspective.
Fisheye Lens: How It Works Mechanically
The magic of Fisheye Lens: How It Works lies in its optical design. Here’s a breakdown of its key components:
1. Curved Front Element
Fisheye Lenses feature a deeply convex front glass element. This curve bends incoming light at extreme angles, allowing the lens to capture light from nearly 180° around the camera.
2. Short Focal Length
Most Fisheye Lenses have a focal length between 8mm and 15mm (for full-frame cameras). This short focal length compresses the field of view, squeezing a vast scene into a single frame.
3. Complex Lens Arrangement
Inside the lens, multiple aspherical and extra-low dispersion (ED) elements correct chromatic aberration and maintain sharpness across the frame. Some designs use up to 10 lens elements to balance distortion and image quality.
4. Distortion as a Feature
Unlike traditional lenses, which aim to minimize distortion, Fisheye Lenses intentionally exaggerate it. This creates a surreal, almost 3D effect that draws viewers into the image.
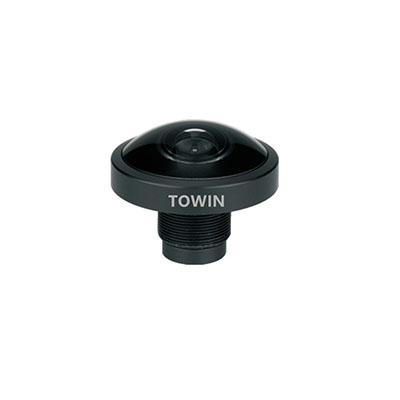
4-Megapixel F2.4 M12 mount fisheye lens
Creative Applications of Fisheye Lenses
- Understanding Fisheye Lens: How It Works opens doors to creative experimentation. Here are some popular uses:
- Landscape Photography: Capture sweeping vistas with a sense of depth.
- Action Sports: Emphasize speed and motion by warping the background.
- Architecture: Highlight grand structures with exaggerated curves.
- Abstract Art: Turn mundane objects into dynamic patterns.
- Virtual Reality (VR): Mimic human peripheral vision for immersive experiences.
For example, skateboarders often use Fisheye Lenses to make tricks appear more dramatic, while real estate photographers leverage them to showcase small spaces creatively.
Pros and Cons of Fisheye Lenses
1. Advantages:
- Ultra-wide field of view for unique perspectives.
- Compact size compared to other wide-angle lenses.
- Affordable options for beginners (e.g., the Rokinon 8mm f/3.5).
2. Disadvantages:
- Extreme distortion may not suit all subjects.
- Limited use in portraiture or flat-lay photography.
- Requires careful composition to avoid cluttered frames.
Fisheye Lens: How It Works in Practice
To master Fisheye Lens: How It Works, follow these tips:
- Get Close: Fisheye Lenses excel at macro-like close-ups. Fill the frame with your subject for maximum impact.
- Mind the Horizon: Keep the horizon centered to avoid unnatural tilting.
- Use for Impact: Reserve Fisheye Lenses for scenes where distortion enhances the story.
- Post-Processing: Correct minor issues (e.g., vignetting) in software like Adobe Lightroom.

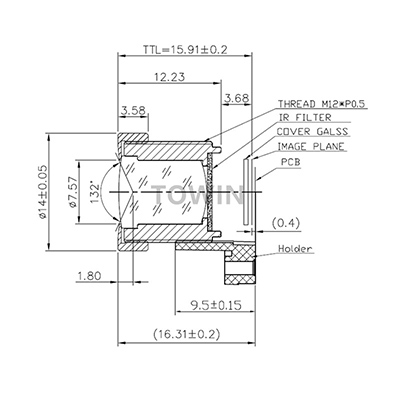
Fisheye IR Cut Filter S-Mount Lens
FAQs
1. What is the difference between a Fisheye Lens and a Wide-Angle Lens?
A Fisheye Lens offers a much wider field of view (180°+) with intentional distortion, while wide-angle lenses (e.g., 24mm) minimize distortion for natural-looking images.
2. Can I use a Fisheye Lens for portraits?
Technically yes, but the distortion may make facial features appear unflattering. It’s better suited for environmental portraits or creative shots.
3. Are Fisheye Lenses only for DSLRs?
No! Many mirrorless cameras and smartphones (via add-on lenses) now support Fisheye effects.
4. How do I avoid lens flare with a Fisheye Lens?
Use a lens hood and shoot away from bright light sources. Post-processing can also reduce flare.
5. Do Fisheye Lenses work well in low light?
Most Fisheye Lenses have wide apertures (e.g., f/2.8), making them usable in low light, but slower models may struggle.
Conclusion
The Fisheye Lens: How It Works is a testament to photography’s boundless creativity. By harnessing its ultra-wide perspective and intentional distortion, you can transform mundane scenes into visually striking narratives.