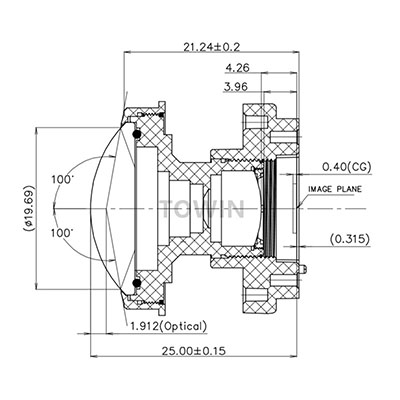
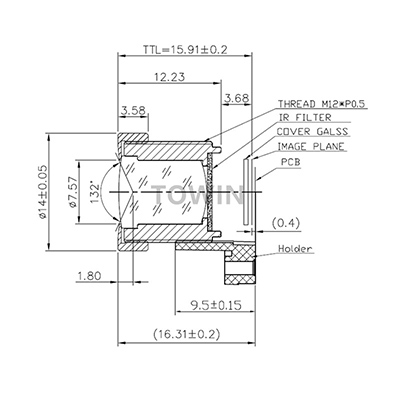
Thermal Stability in Low-Distortion Lenses

Sealed Automotive lens
11/13/2025
High-resolution CS-Mount lenses for machine vision
11/13/2025In the world of optics, one of the most important factors influencing lens performance is thermal stability. This is especially true for low-distortion lenses, which are increasingly popular in various fields such as photography, cinematography, and scientific research. The ability of these lenses to maintain their shape and optical characteristics despite temperature fluctuations plays a crucial role in ensuring image clarity and accuracy.
What Are Low-Distortion Lenses?
Low-distortion lenses are optical lenses designed to minimize or eliminate visual distortions such as barrel or pincushion distortion. These types of lenses are particularly useful in applications that require high precision, such as architectural photography, surveying, and optical testing. The goal of low-distortion lenses is to produce images that are as true to reality as possible, without warping straight lines or objects.
The design of these lenses often involves complex glass formulations and precise manufacturing processes. Thermal stability is a critical aspect of their design, ensuring that the lens retains its shape and optical properties even in environments with varying temperatures.
Why Is Thermal Stability Crucial in Low-Distortion Lenses?
Thermal stability in low-distortion lenses refers to the lens’s ability to withstand temperature changes without significant degradation in its optical performance. Temperature fluctuations can cause materials to expand or contract, which in turn can affect the focal length, image sharpness, and the overall distortion of the lens.
1. Maintaining Optical Accuracy
When a lens experiences thermal expansion or contraction, it can lead to changes in the curvature of the lens elements. This can distort the image produced by the lens, leading to a loss of clarity and sharpness. For low-distortion lenses, this is particularly problematic as the very design of the lens aims to keep distortion to a minimum. Thermal stability helps maintain the precise curvature of the lens elements, ensuring that the optical performance remains consistent across a range of temperatures.
2. Enhanced Durability
Low-distortion lenses often feature high-quality materials that are designed to withstand the stresses of everyday use. However, extreme temperatures can still cause materials to weaken or degrade over time. Thermal stability ensures that these lenses can withstand changes in temperature without significant damage, increasing their lifespan and reliability.
3. Consistent Image Quality
In practical applications, such as when shooting in outdoor environments or using lenses in changing temperatures, thermal stability ensures that image quality remains consistent. Whether you’re working in a hot desert or a cold mountain, your low-distortion lens will deliver the same level of clarity and accuracy.

low-distortion C-mount lens
Factors That Affect Thermal Stability in Low-Distortion Lenses
Several factors contribute to the thermal stability of low-distortion lenses, including the materials used, the lens design, and the manufacturing processes involved.
1. Material Selection
The choice of materials is one of the most important factors in ensuring thermal stability in low-distortion lenses. Lenses are typically made from glass or synthetic materials, and each has its own thermal properties. Materials with low coefficients of thermal expansion (CTE) are preferred, as they are less likely to expand or contract with temperature changes. For example, certain types of optical glass and advanced polymers are commonly used in low-distortion lenses due to their excellent thermal stability.
2. Lens Coatings and Treatments
In addition to the lens materials themselves, coatings and treatments applied to the lens can also play a role in its thermal stability. Anti-reflective coatings, for instance, not only improve light transmission and reduce glare but can also help protect the lens from the effects of temperature changes. Special coatings can also help prevent fogging or condensation that might occur during sudden temperature shifts.
3. Lens Design
The design of the lens, including the shape and positioning of individual lens elements, can impact its thermal stability. Lenses designed with multiple elements must be carefully aligned to ensure minimal distortion even under temperature fluctuations. The use of materials with varying thermal properties must be balanced in such a way that the lens elements move in sync to avoid any misalignment that could lead to distortion.
4. Manufacturing Precision
High-precision manufacturing techniques are crucial for ensuring the thermal stability of low-distortion lenses. Even slight imperfections or misalignments during production can affect the lens’s ability to maintain its shape under varying temperatures. The use of advanced manufacturing technologies, such as computer-aided design (CAD) and robotic assembly, can help achieve the level of precision needed for optimal thermal stability.
Low distortion lens 12-Megapixel M12 F2.2 CCTV lens
Challenges in Achieving Thermal Stability in Low-Distortion Lenses
Despite advancements in lens technology, achieving optimal thermal stability in low-distortion lenses presents several challenges:
1. Material Compatibility
Combining materials with different thermal expansion rates can result in optical misalignment or distortion. Ensuring that all materials used in the lens elements expand and contract at the same rate is a complex process that requires careful selection and testing of materials.
2. Cost
High-quality materials and manufacturing processes designed for optimal thermal stability often come with a higher cost. Lenses that are engineered for extreme thermal stability tend to be more expensive, which can limit their accessibility for certain applications.
3. Environmental Factors
External environmental factors, such as humidity and pressure, can also affect the thermal stability of low-distortion lenses. While most lenses are designed to function under a range of temperatures, extreme conditions may still cause performance degradation, especially in lenses that are not built with the highest thermal stability in mind.
How to Choose Low-Distortion Lenses with Excellent Thermal Stability
When selecting low-distortion lenses for your specific needs, it’s important to consider the following:
1. Check the Lens Specifications
Ensure that the lens you’re considering is designed to maintain its performance under varying temperature conditions. Look for lenses that explicitly mention thermal stability as a key feature.
2. Consider the Lens Materials
Opt for lenses made from materials known for their low thermal expansion rates. High-end optical glass and advanced polymers are good indicators of a lens’s ability to handle temperature changes.
3. Research Reviews and Tests
Look for reviews or technical tests that assess the thermal stability of the lens in real-world conditions. This can give you an idea of how well the lens will perform in different environments.

25mm Low Distortion Machine Vision Lens
FAQs
1. What is the impact of temperature changes on low-distortion lenses?
Temperature changes can cause low-distortion lenses to deform, leading to image distortion or a loss of optical accuracy. Thermal stability ensures that the lens maintains its shape and clarity even in fluctuating temperatures.
2. How can I test the thermal stability of a lens?
Thermal stability tests can be conducted by subjecting the lens to various temperature conditions and measuring its performance in terms of image clarity, distortion, and focus accuracy.
3. Are all low-distortion lenses thermally stable?
Not all low-distortion lenses are equally thermally stable. Lenses with higher quality materials and precise manufacturing processes tend to have better thermal stability.
Conclusion
Thermal stability in low-distortion lenses is a critical factor that ensures consistent performance and optical accuracy in varying environmental conditions. By understanding the importance of thermal stability, the factors that contribute to it, and how to select the right lenses, you can make informed decisions when investing in high-quality low-distortion lenses for your specific needs.