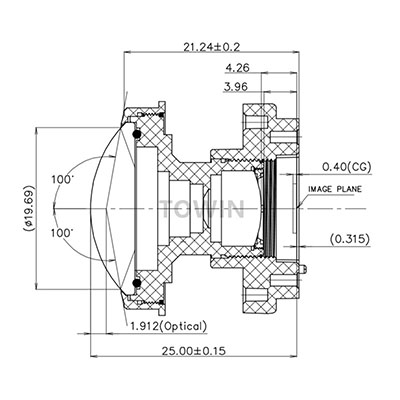
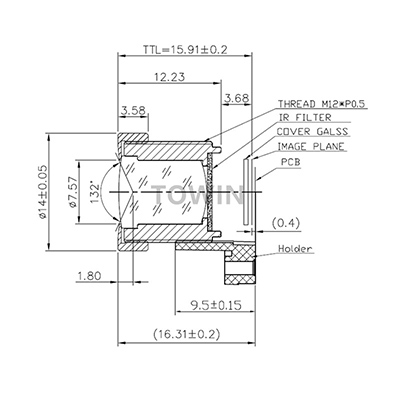
Industrial Lens Aperture Size Guide

F1.2 2.1mm IR corrected CCTV CS-mount lens
10/11/2025
Standard vs Aspherical ITS Lens
10/13/2025Choosing the right Industrial Lens Aperture Size is critical for achieving sharp images, controlling light intake, and ensuring reliability in industrial applications. Whether you’re working in machine vision, quality inspection, or robotics, understanding how aperture size impacts performance can save time, reduce costs, and enhance efficiency.
What Is an Industrial Lens Aperture?
The aperture of an Industrial Lens is the adjustable opening that regulates the amount of light reaching the camera sensor. Measured in f-stops (e.g., f/2.8, f/8), a smaller f-number indicates a wider aperture, allowing more light in, while a larger f-number narrows the opening. In industrial settings, aperture size directly affects depth of field, exposure, and image clarity, making it a pivotal factor in system design.
Why Aperture Size Matters in Industrial Applications
- Light Control: Industrial environments often have varying lighting conditions. A wider aperture (e.g., f/1.4) suits low-light scenarios, while a narrower aperture (e.g., f/16) prevents overexposure in bright settings.
- Depth of Field (DoF): A smaller aperture (higher f-number) increases DoF, ensuring more of the scene is in focus—critical for inspecting detailed components. Conversely, a wider aperture isolates subjects but reduces DoF.
- Image Sharpness: Stopping down the lens (using a mid-range aperture like f/8) often yields the sharpest images by minimizing lens aberrations.
- Motion Blur Prevention: Faster shutter speeds paired with wider apertures reduce motion blur in high-speed industrial processes.

12-50mm-P-Iris-CS-Mount Industrial lenses
Industrial Lens Aperture Size Guide: 5 Key Considerations
1. Application Requirements
- Machine Vision: Systems inspecting small defects (e.g., semiconductor chips) need high DoF, favoring narrower apertures (f/11–f/16).
- Robotics: Fast-moving robots require wider apertures (f/2.8–f/4) to capture motion without blur.
- Surveillance: Low-light environments demand lenses with adjustable apertures to adapt to lighting changes.
2. Sensor Sensitivity
High-resolution industrial cameras with advanced sensors may perform well in low light, allowing narrower apertures. Conversely, older sensors might rely on wider apertures to compensate for limited sensitivity.
3. Working Distance
The distance between the lens and the object affects aperture choice. Longer working distances may require wider apertures to gather sufficient light, while shorter distances allow for narrower settings.
4. Environmental Factors
Dust, vibrations, or extreme temperatures can impact lens performance. Sealed industrial lenses with fixed apertures may be preferable in harsh conditions to prevent debris ingress.
5. Cost vs. Performance
Variable-aperture lenses offer flexibility but are pricier. Fixed-aperture lenses are cost-effective for applications with consistent lighting.
How to Choose the Right Aperture Size
- Test Under Real Conditions: Simulate your industrial environment to evaluate aperture performance.
- Prioritize DoF Needs: If inspecting 3D objects, prioritize narrower apertures for greater DoF.
- Balance Light and Speed: For high-speed applications, use wider apertures with faster shutter speeds.
- Consult Manufacturer Data: Review lens specifications for optimal aperture ranges.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Overusing Wide Apertures: While they gather more light, they reduce DoF, potentially missing defects.
- Ignoring Environmental Constraints: Dust or moisture can damage adjustable aperture mechanisms.
- Neglecting Sensor Compatibility: Pairing a high-resolution sensor with a lens that can’t resolve fine details wastes resources.

50mm-C-mount industrial lens
FAQs
1. What is the best aperture size for machine vision?
For most machine vision tasks, an aperture between f/8 and f/11 provides a balance of sharpness and DoF. However, adjust based on lighting and working distance.
2. Can I use a consumer lens for industrial applications?
No. Industrial lenses are designed for durability, precision, and compatibility with machine vision software. Consumer lenses lack the ruggedness and calibration needed for industrial settings.
3. How does aperture affect image noise?
Wider apertures let in more light, reducing the need for high ISO settings, which can introduce noise. However, extremely wide apertures may cause lens aberrations, degrading image quality.
4. What is the relationship between aperture and shutter speed?
A wider aperture allows faster shutter speeds by increasing light intake, which is crucial for capturing fast-moving objects. Conversely, narrower apertures require slower shutter speeds, risking motion blur.
5. Are fixed-aperture lenses better than variable ones?
It depends on the application. Fixed-aperture lenses are simpler and more reliable in harsh environments, while variable-aperture lenses offer flexibility for dynamic lighting conditions.
Conclusion
Selecting the right Industrial Lens Aperture Size is a blend of science and practicality. By evaluating application needs, environmental factors, and sensor capabilities, you can optimize image quality, reduce errors, and enhance productivity.