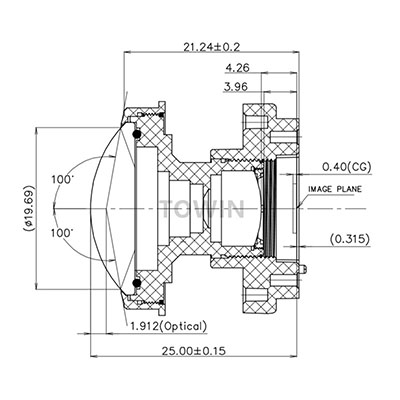
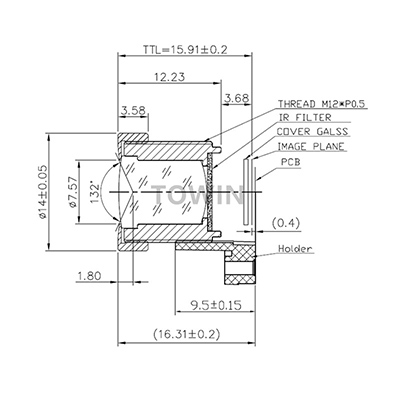
Understanding Low-Distortion Lenses

20MP 12mm low distorton C-mount FA lens
09/18/2025
Affordable Fisheye Lens for Educational Purposes
09/19/2025In photography, cinematography, and industrial imaging, Understanding Low-Distortion Lenses is critical for achieving sharp, accurate results. Unlike standard lenses, which may introduce warping or blurring, low-distortion lenses minimize optical aberrations, ensuring that straight lines remain straight and details stay crisp.
What Causes Distortion in Lenses?
Distortion occurs when light rays bend unevenly through a lens, stretching or compressing parts of an image. Two common types are barrel distortion (where edges bulge outward) and pincushion distortion (where edges pinch inward). Low-distortion lenses combat these issues through advanced design elements like aspherical glass and multi-element coatings, which correct light paths before they reach the sensor.
5 Key Benefits of Low-Distortion Lenses
- 1. Architectural Precision: Perfect for real estate photography or engineering surveys, these lenses preserve straight lines in buildings and structures.
- 2. Enhanced Detail Retention: In medical imaging or machine vision, even minor distortions can mislead diagnoses or quality checks. Low-distortion lenses eliminate this risk.
- 3. Seamless Stitching: For panoramic shots or 3D modeling, distortion-free lenses ensure overlapping images align flawlessly.
- 4. Reduced Post-Processing Time: By capturing cleaner images upfront, these lenses save hours of manual corrections in software like Photoshop or Lightroom.
- 5. Consistent Performance Across Focal Lengths: Whether zoomed in or out, low-distortion lenses maintain geometric accuracy, unlike some variable-focus alternatives.

IR 12MP Low Distortion Machine Vision Lens
Real-World Applications
From drones mapping landscapes to smartphones capturing selfies, low-distortion lenses are revolutionizing industries. For instance, in augmented reality (AR), they ensure virtual objects align correctly with the real world. Similarly, automotive LIDAR systems rely on distortion-free optics to detect obstacles accurately.
How to Choose the Right Low-Distortion Lens
When selecting a lens, prioritize:
- Aspherical Elements: These reduce spherical aberration, a common distortion source.
- Coating Quality: Anti-reflective coatings improve light transmission and contrast.
- Focal Length Range: Wide-angle lenses are more prone to distortion; opt for models designed specifically for low distortion.
For technical specifications, consult resources like Edmund Optics, a trusted provider of precision optics.
The Future of Low-Distortion Optics
Advancements in computational photography and metamaterials are pushing the boundaries of what low-distortion lenses can achieve. Future designs may integrate AI-driven correction algorithms or nanostructured glass to eliminate distortion entirely.

Megapixel lens Low Distortion lens
Conclusion
Understanding Low-Distortion Lenses unlocks a world of possibilities for professionals who refuse to compromise on image quality. By investing in these advanced optics, you’re not just buying a lens—you’re securing a tool that transforms ambiguity into clarity. Whether you’re a photographer, engineer, or scientist, the benefits of low-distortion lenses are undeniable: they’re the cornerstone of precision in an imperfect world.