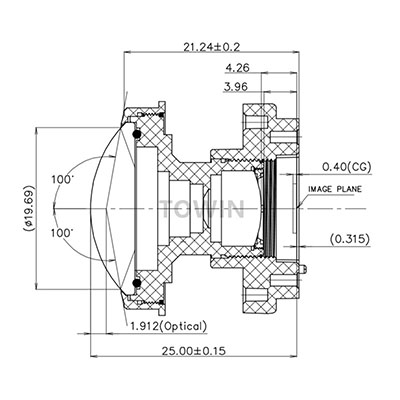
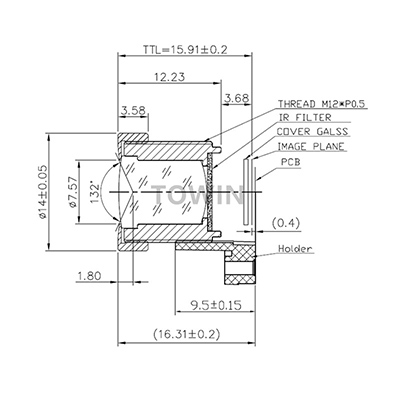
Aperture size impact machine vision lenses

Lockable Focus ITS Lens: Tamper-Proof
11/20/2025
Fisheye Lens vs. Ultra-Wide Lens
11/20/2025When it comes to machine vision systems, understanding the role of aperture size in lenses is crucial. The aperture is the opening in the lens through which light enters, and its size can significantly influence the performance and image quality of a machine vision system.
Understanding the Role of Aperture Size in Machine Vision Lenses
Machine vision lenses are designed to capture and process visual data for a wide range of industrial, scientific, and commercial applications. The aperture size directly affects how much light enters the lens, which in turn impacts the brightness, depth of field, and clarity of the image captured by the system. This can influence the ability of the system to detect small defects, measure distances accurately, or navigate in low-light environments.
In general, a larger aperture allows more light to pass through, which is beneficial in low-light conditions. A smaller aperture, on the other hand, reduces the amount of light entering the lens but increases the depth of field, making it ideal for applications requiring high precision and clear focus across a wide range of distances.

40mm C mount IR corrected machine vision lenses
How Does Aperture Size Impact Machine Vision Lenses in Practical Applications?
1. Impact on Depth of Field
Depth of field refers to the range of distance within which objects appear sharply focused. In machine vision systems, depth of field is essential for ensuring that all objects, regardless of their position within the field of view, are within focus. A small aperture (high f-number) increases the depth of field, making it easier to capture objects at different distances in focus simultaneously. This is particularly useful in applications such as inspecting products on a production line or scanning large areas for defects.
2. Effect on Image Brightness and Low-Light Performance
A larger aperture (low f-number) allows more light to enter the lens, resulting in brighter images. This is especially beneficial in environments where lighting conditions are poor or in applications that require high-speed image capture, such as industrial inspections or high-speed automated sorting systems. With brighter images, machine vision systems can operate more efficiently in low-light conditions, improving accuracy and performance.
3. Impact on Motion Blur and Speed
Larger apertures allow faster shutter speeds, which is essential when capturing moving objects. A fast-moving object can blur if the lens’s aperture is too small. By using a larger aperture, machine vision systems can capture crisp images of moving objects, making them ideal for applications in robotics or high-speed inspection lines.
4. Aperture and Optical Aberrations
The size of the aperture can also affect optical aberrations like distortion and chromatic aberration. Smaller apertures can reduce these distortions but may lead to diffraction, which can slightly degrade image sharpness. On the other hand, large apertures can introduce more optical distortions but often deliver sharper images in the center of the field of view. Balancing aperture size and lens quality is key to obtaining the best image clarity for specific tasks.

IR 12MP Low Distortion Machine Vision Lens
How Does Aperture Size Impact Machine Vision Lenses in Different Industrial Applications?
- Automated Quality Inspection: In automated quality inspection, machine vision systems must be able to detect minute defects on products. A larger aperture allows more light to reach the sensor, enabling the system to detect small defects even in dimly lit environments. On the other hand, a smaller aperture might be used in cases where the entire surface of the product needs to be in focus.
- Robotics and Autonomous Vehicles: Machine vision plays a significant role in robotics and autonomous vehicles by helping them navigate and avoid obstacles. A larger aperture improves low-light performance, allowing the system to see clearly in dark or poorly lit areas. However, in systems where precise measurements and depth are critical, smaller apertures might be preferred to increase the depth of field.
- Medical Imaging: In medical imaging systems, machine vision lenses must capture high-resolution images for accurate diagnostics. A smaller aperture can be used to enhance the depth of field, ensuring that multiple layers or regions within the sample are in focus simultaneously. This is particularly important in applications like microscopy or tissue analysis.
Choosing the Right Aperture for Your Machine Vision Lens
Selecting the right aperture size depends on the specific requirements of the application. If your application involves high-speed operations or low-light conditions, a larger aperture may be necessary. For applications that demand high precision and wide depth of field, such as automated inspection or measurement tasks, a smaller aperture would be the better choice.
Consider the following factors when choosing the appropriate aperture for your machine vision lens:
- Lighting conditions: For low-light environments, opt for a lens with a larger aperture.
- Speed of the system: For high-speed applications, such as robotics or moving object detection, a larger aperture will help reduce motion blur.
- Depth of field: If the focus needs to extend across a wide range of distances, choose a smaller aperture to increase the depth of field.
FAQs
How does aperture size affect the image sharpness of machine vision lenses?
The aperture size influences image sharpness by controlling how much light enters the lens. A larger aperture can produce sharper images in low-light environments but may reduce depth of field and increase optical aberrations. Smaller apertures improve depth of field and reduce distortions, resulting in clearer images across various distances.
Can a smaller aperture improve image quality in bright environments?
Yes, a smaller aperture can enhance image quality in bright environments by reducing the amount of light entering the lens. This can prevent overexposure and improve contrast in well-lit conditions, making it ideal for applications requiring high precision.
What is the best aperture size for machine vision systems in low-light conditions?
For low-light conditions, a larger aperture (low f-number) is typically preferred as it allows more light to enter the lens, improving image brightness and clarity.
Are there any trade-offs when using a larger aperture in machine vision lenses?
Yes, while a larger aperture allows more light to pass through, it can also reduce the depth of field, meaning that only objects within a specific range of distances will appear in focus. Additionally, larger apertures may introduce optical distortions like chromatic aberration.
How does aperture size impact the speed of a machine vision system?
A larger aperture allows faster shutter speeds, which is crucial for capturing moving objects without motion blur. This is particularly important in high-speed machine vision systems, such as those used in industrial automation or robotics.

25mm Low Distortion Machine Vision Lens
Conclusion
Aperture size impact machine vision lenses? Aperture size plays a critical role in the performance of machine vision lenses. Whether you’re working in manufacturing, robotics, medical imaging, or any other field that relies on machine vision systems, understanding how aperture size impacts the quality, depth of field, and brightness of your images can help you choose the right lens for your needs.